Novel Cathode for Lithium-Sulfur Battery (No. 0203)
|
|
<< Back to all technologies |
Summary
A novel cathode that provides high energy capacity and long cyclic stability simultaneously for lithium sulfur (Li-S) battery.
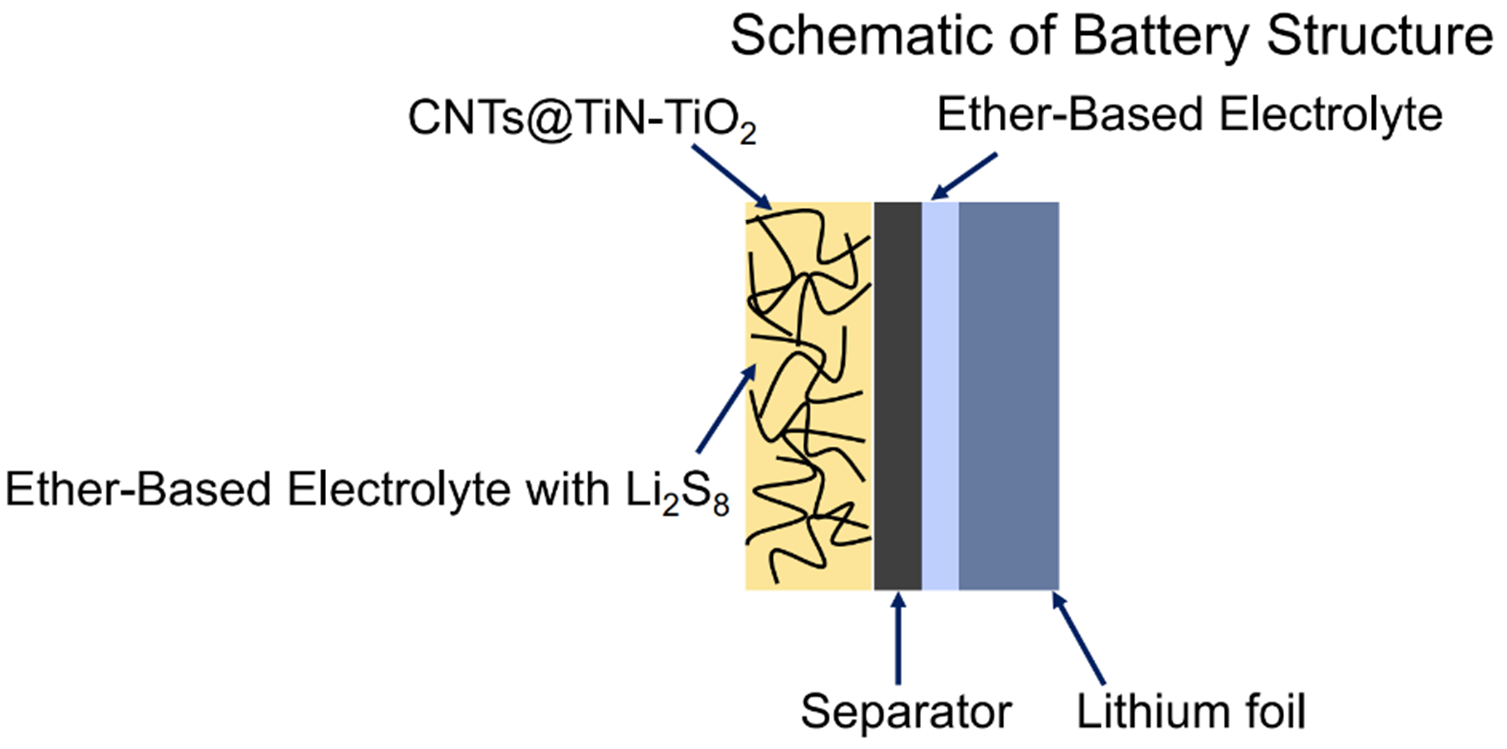
The global Li-S battery market size is projected to reach USD 6.6 Billion, at a CAGR of 29.6%. Li-S batteries are mainly projected to be used in aviation, automotive, electronic device, and power & energy sector due to the growing demand for light weight and higher energy density battery types. However, current Li-S batteries have problems with sulfur loading and polysulfide dissolution & shuttling. Here we present a promising cathode developed by a group of researchers led by Prof. Yabing Qi. The cathode is a carbon nanotube (CNT) sponge whose surface is optimally deposited with TiN and TiO2 layers. As a result of this cathode structure, the Li-S battery overcomes the above problems and has improved areal capacity (energy density) and long cyclic stability simultaneously.
Applications
- Lithium sulfur battery
Advantages
- High areal capacity
- Long cyclic stability
- High sulfur loading
Technology
The technology is based on a novel method for depositing, by atomic layer deposition (ALD), precise cathode TiN-TiO2 heterostructure layers on a three-dimensional (3D) conductive carbon nanotube (CNT) sponge scaffold. The TiN-TiO2 heterostructure by ALD can be optimized in nanometer scale. As a result, long cyclic stability (85% capacity retention after 500 cycles at a 1.0 charge rate) and high areal capacity (20.5 mAh cm-2 at a 0.2 charge rate) are achieved for a Li-S battery.
Media Coverage and Presentations
CONTACT FOR MORE INFORMATION
![]() Graham Garner
Graham Garner
Technology Licensing Section
![]() tls@oist.jp
tls@oist.jp
![]() +81(0)98-966-8937
+81(0)98-966-8937