Organocatalytic Synthesis of Functionalized Dihydropyrans from Pyruvates in a One-Pot Reaction (No. 0022)
|
|
|
<< Back to all technologies |
Summary
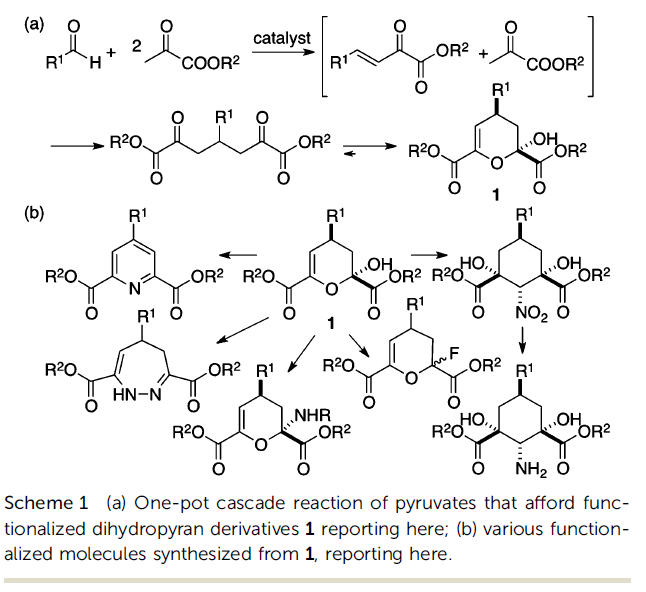
Dihydropyrans are an important category of compounds, as the structure is present in a variety of pharmaceutical products, as well as other bioactive molecules. Dihydropyran derivatives are commonly synthesized through the non-catalytic reaction of pyruvates at high temperatures, which makes it difficult to control the dual electrophilic/nucleophilic reactivity of pyruvates. Furthermore, this synthetic approach does not allow further functionalization of the product in one pot. A team of OIST researchers led by Prof. Fujie Tanaka has developed a novel, catalytic synthetic route to produce a wide variety of dihydropyran derivatives in one pot from pyruvates and aldehydes, under mild conditions and with high yields and diastereoselectivity.
Applications
- Drug discovery
- Therapeutic medicine
Advantages
- A simple, one-pot process
- Mild conditions (room temperature
- High yield and diastereoselectivity
- Large library of potential compounds
Technology
The researchers showed that the dual reactivities of pyruvates can be managed by using an appropriate catalyst and tuning the reaction conditions, to generate functionalized dihydropyran derivatives in non-enzymatic reactions. The products can be further modified in a one-pot cascade reaction to generate various functionalized molecules. Among the several organocatalysts tested, pyrrolidine-3-carboxylic acid (β-proline) was found to be the best-performing. The optimized reaction was conducted using ethyl pyruvate, aldehyde, and β-proline in CH3CN at 250 oC. Under these conditions, the dihydropyran product was obtained in 72% yield as a single diastereomer.
Media Coverage and Presentations
CONTACT FOR MORE INFORMATION
![]() Paola Butler-Zanetti
Paola Butler-Zanetti
Technology Licensing Section
![]() tls@oist.jp
tls@oist.jp
![]() +81(0)98-966-8937
+81(0)98-966-8937