Microfluidics and Rheology
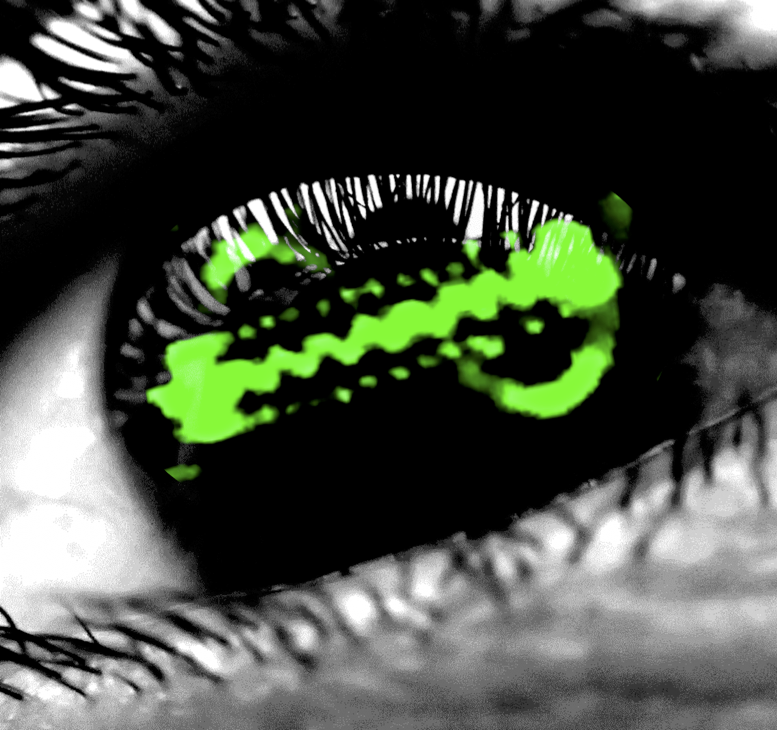
Viscoelastic and inertio-elastic instabilities in microfluidics
A number of important applications exploit the ability of high molecular weight polymers to modify flow instabilities and create new ones that are absent in Newtonian fluids. At very low Reynolds numbers, polymers can enhance mixing in microdevices. When inertia is important, at higher Reynolds number, some of the most dramatic effects are turbulent drag reduction, suppression of jet breakup and improvement of oilfield sweep in enhanced oil recovery.
Vortex breakdown and vortex dynamics inside microfluidics
1. Vortex breakdown in a microfluidic dividing T-channel
2. Coupling of vortex breakdown and stability in a swirling flow
3. Controlled symmetry breaking and vortex dynamics in intersecting flows
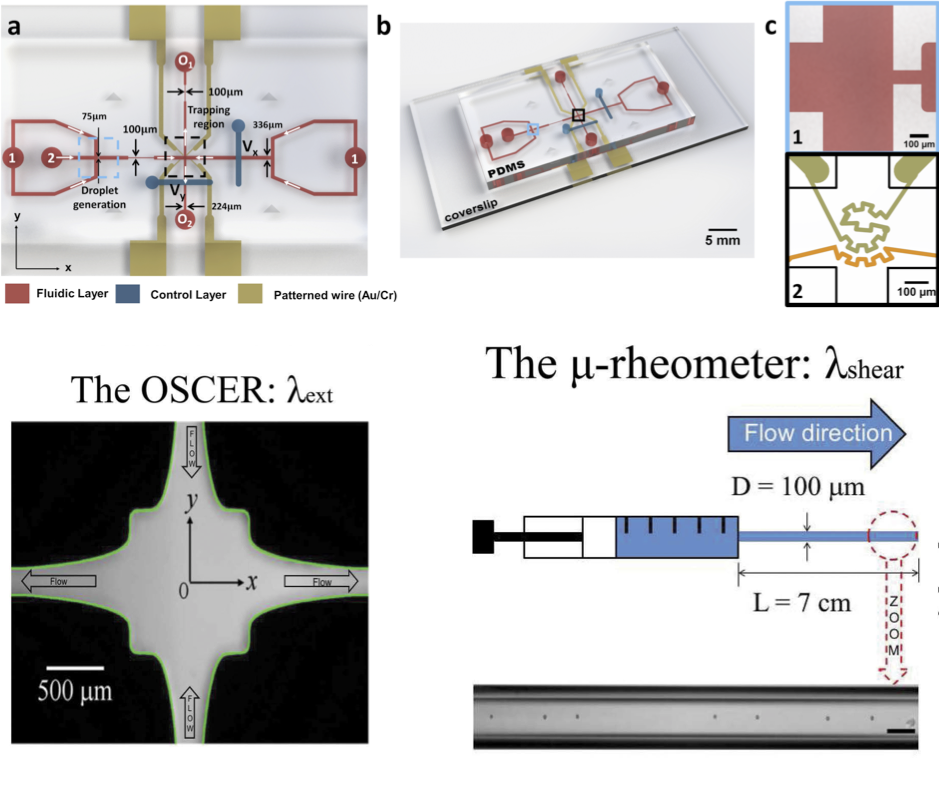
Microfluidics assisted materials characterizations
Microfluidics serves as a versatile platform of handling tiny amount of fluids at small length-scales, and in particular, manipulating fluids under precise temperature and flow conditions. We recently developed integrated microfluidic platforms serving as micro-rheometers to measure small relaxation times of dilute polymer solutions, or temperature sensitive tensiometer for precise interfacial tension measurements.
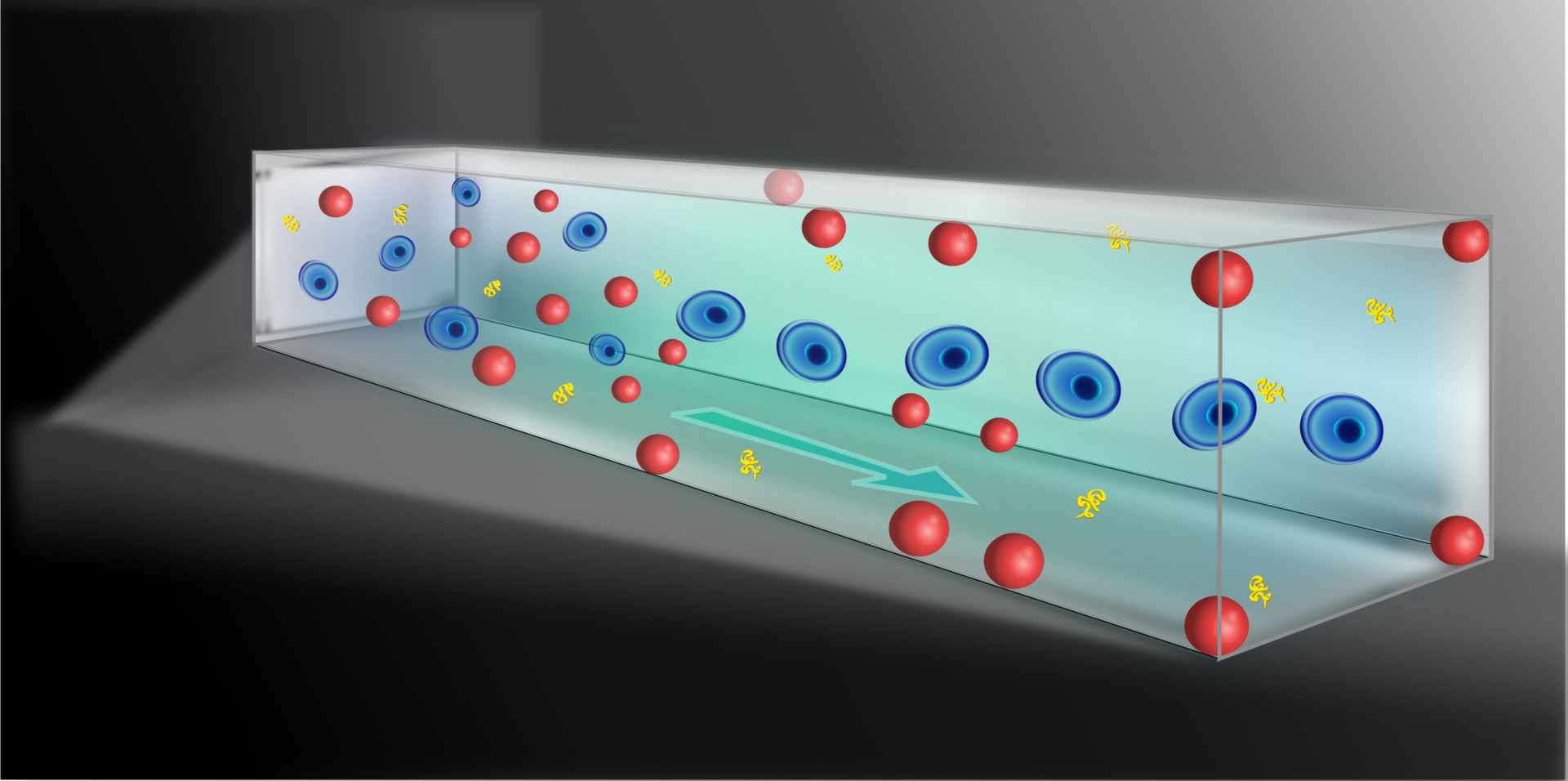
Particle production and manipulation in microfludics
Microfluidic platforms have been widely used for particle generation and manipulations. We use viscoelastic fluids in a straight microchannel to focus and order particles and cells; and use flow flocusing device to make nanoparticles.
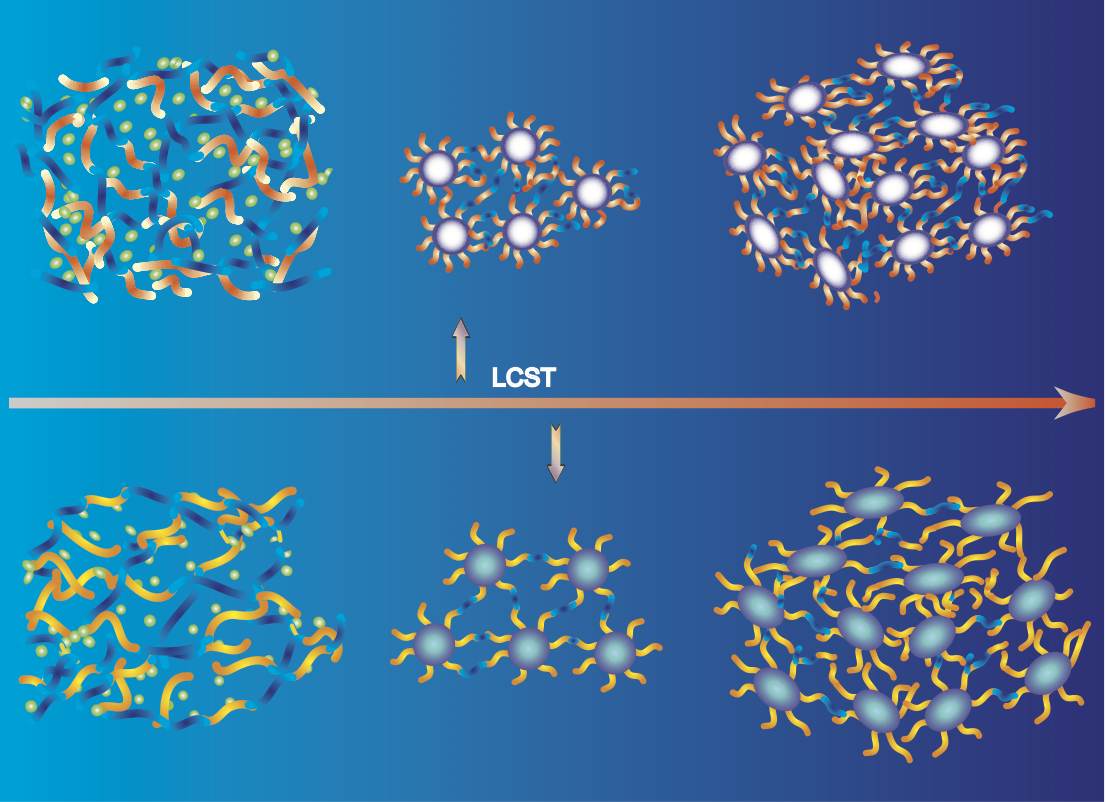
Rheology of complex fluids
Our lab is well equipped with various shear and extensional rheometers and custom designed microfluidic rheometers to investigate rhological behavior of complex fluids.




