FY2022 Annual Report
Femtosecond Spectroscopy Unit
Full Professor Keshav Dani

Abstract
In recent years, the ability to synthesize, engineer & observe low-dimensional materials, with properties determined by variations on the nanometer length scale, has led to novel phenomena and applications. On the other hand, modern lasers deliver powerful, ultrashort pulses of light allowing us to observe the interaction of electrons and atoms on the femtosecond timescale. Together, these technologies allow us to study new paradigms in light-matter interaction – with femtosecond temporal resolution and nanometer spatial resolution. In FY2022, Femtosecond Spectroscopy Unit has directed these broad capabilities towards two different areas of study:
- Energy Materials, where we study the nature of defects in perovskite photovoltaic materials, and the synthesis of TiO2 with the potential for photocatalytic activity in the visible.
- Terahertz Devices and Applications, where we study the optimum excitation wavelength for spintronic terahertz emission from Fe/Pt bilayer.
1. Staff
- Dr. Keshav M. Dani, Professor
- Dr. Michael M. Man, Researcher
- Dr. Julien Madéo, Researcher
- Dr. Arka Karmakar, Researcher
- Dr. David Bacon, Researcher
- Dr. Filchito Renee Bagsican, Researcher
- Dr. Jacques Hawecker, Researcher
- Dr. Viktoras Lisicovas, Technology Pioneer Fellow
- Vivek Pareek, Graduate Student
- Sofiia (Sonya) Kosar, Graduate Student
- Xing Zhu, Graduate Student
- Maria-Carla Lupu, Graduate Student
- Prajakta Kokate, Graduate Student
- Yumi Ito, Administrative Assistant
2. Collaborations
Theme: Energy Materials
Type of Collaboration: Joint Research
- Researchers:
- S.D. Stranks, Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK
- Paul A. Midgley, Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK
Theme: Terahertz Devices and Applications
Type of Collaboration: Joint Research
- Researchers:
- M. Tani, Research Center for Development of Far-Infrared Region, University of Fukui, Japan
3. Activities and Findings
3. Activities and Findings
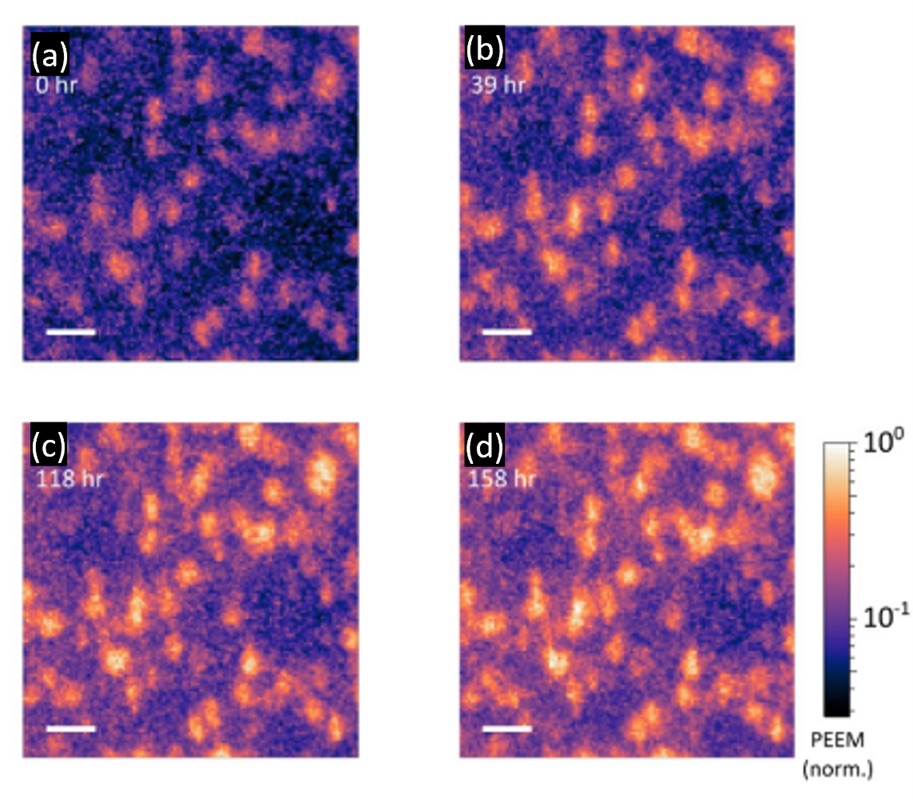
A. Local nanoscale phase impurities are degradation sites in halide perovskites
[Nature 607, 294-300 (2022)]
Understanding the nanoscopic chemical and structural changes that trigger instabilities in emerging halide perovskite photovoltaic materials is crucial for mitigating device degradation. Although reaching a power conversion efficiency of 25.7% in single-junction cells and 29.8% in tandem perovskite/silicon cells [1-2], to maintain such performance during continuous operation has proven challenging [3]. In this study, we have developed a comprehensive microscopy toolkit that employs multiple imaging techniques. Our investigation reveals that formamidinium-rich perovskite absorbers contain nanoscale phase impurities. These impurities, such as hexagonal polytype and lead iodide inclusions, not only act as traps for photoexcited carriers, thereby reducing performance, but also serve as sites where photochemical degradation of the absorber layer initiates [4-5]. We observe structural changes at these phase impurities induced by illumination, particularly in trap clusters. It becomes evident that even small amounts of these structural changes, which is undetectable through bulk measurements, could compromise the longevity of the devices. The specific type and distribution of these undesirable phase inclusions depend on the composition and processing of the film, with polytypes having the most detrimental impact on the film's photo-stability. Notably, our findings demonstrate that both performance losses and intrinsic degradation processes can be mitigated by modulating these defective phase impurities. This requires careful adjustment of the local structural and chemical properties. The multimodal workflow we have developed to investigate the nanoscale characteristics of sensitive energy materials can be applied to a wide range of semiconductors.
References Section 3.A:
[1] Best research-cell efficiency chart. NREL, https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell-efficiency.html (2022).
[2] Jošt, M., et al. Monolithic perovskite tandem solar cells: a review of the present status and advanced characterization methods toward 30% efficiency, Adv. Energy Mater. 10, 1904102 (2020).
[3] Li, N., et al. Towards commercialization: the operational stability of perovskite solar cells, Chem. Soc. Rev. 49, 8235–8286 (2020).
[4] Miller, O. D., et al. Strong internal and external luminescence as solar cells approach the Shockley–Queisser limit, J. Photovolt. 2, 303–311 (2012).
[5] Doherty, T. A. S., et al. Performance-limiting nanoscale trap clusters at grain junctions in halide perovskites, Nature 580, 360–366 (2020).
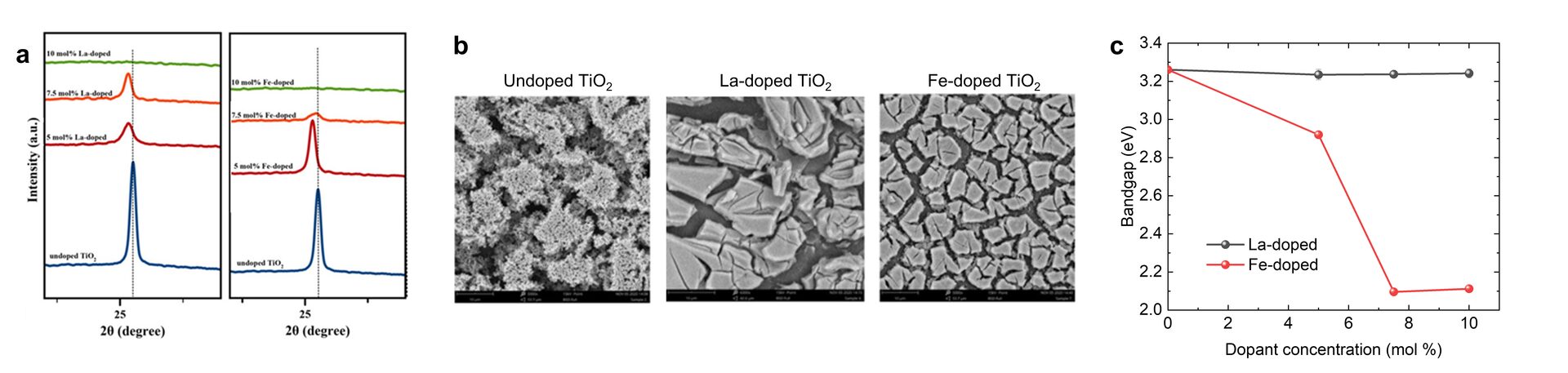
B. Phase Composition, Microstructure, and Optical Characteristics of Spin-Coated La-TiO2 and Fe–TiO2
[Phys. Status Solidi A, 2200756 (2023)]
Titanium oxide (TiO2) is a potentially important material for energy and environmental-related applications due to its high photoactivity, stability, and low toxicity. Several methods have been successfully applied in lowering its bandgap to the visible region (1.7-3 eV), however, most of these processes are complex and not cost-effective. In this work, we developed an acid catalyst-free method which is straightforward yet economical and highly effective in synthesizing TiO2 with a bandgap in the visible region. Furthermore, our method is compatible with the spin-coating technique which allows the fabrication of large area TiO2 films at a low cost.
Our method uses lanthanum (La) and iron (Fe) ions to modify the bandgap of TiO2. We systematically studied the effects of these dopants on the structural and optical properties (Figs. 1a-c) of TiO2 to understand the underlying reaction mechanism in our synthesis method.
References Section 3.B:
[1] M.R.D. Khaki, et al., Application of doped photocatalysts for organic pollutant degradation - A review, J. Environ. Manage. 198, 78-94 (2017).
[2] R. Dahrir, et al., Modified TiO2 For Environmental Photocatalytic Applications: A Review, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52, 3581–3599 (2013).
3.2 Terahertz Devices and Applications
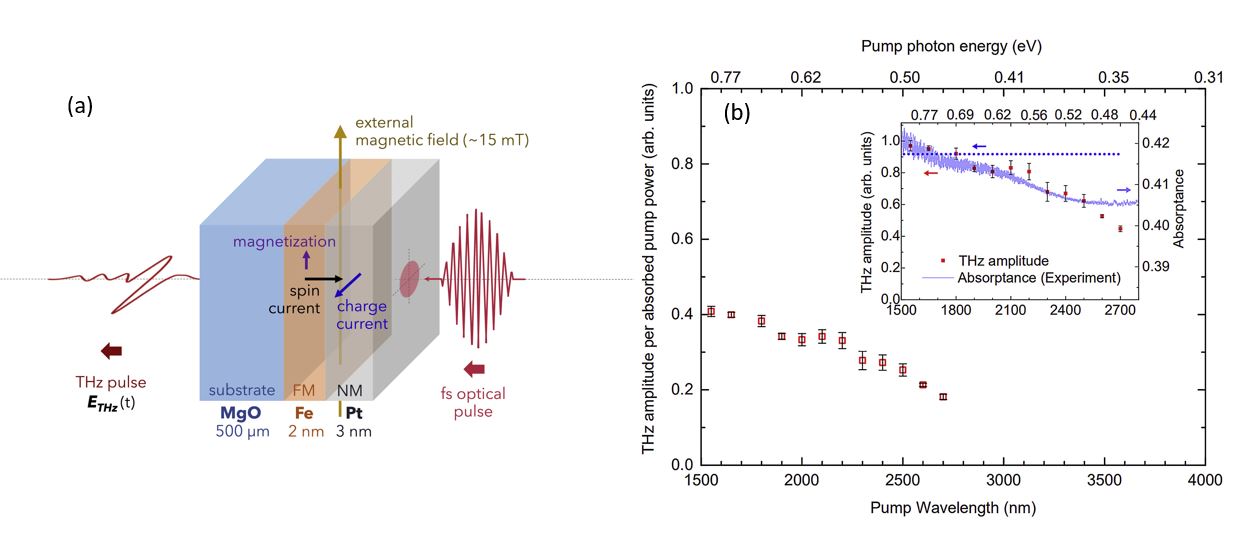
A. Optimum excitation wavelength and photon energy threshold for spintronic terahertz emission from Fe/Pt bilayer
[iScience 25, 104615 (2022)]
Terahertz emission from ferromagnetic/non-magnetic spintronic heterostructures had been demonstrated as pump wavelength independent. In this work, we show a pump wavelength dependence of terahertz emission from an optimized Fe/Pt spintronic bilayer on MgO substrate. Maximum terahertz generation was observed in the 1200- to 1800-nm pump wavelength range, and a clear decrease in the terahertz emission efficiency beyond 2500 nm suggests a ∼0.35-eV threshold pump photon energy for effective spintronic terahertz emission. The inferred threshold is supported by previous theoretical predictions on the onset energy enabling spin-filtering at the Fe-Pt interface [2] and is confirmed by our Fe/Pt electronic structure calculations. The results of terahertz time-domain emission spectroscopy show the sensitivity of spintronic terahertz emission to both the optical absorptance of the heterostructure and the energy-dependent spin transport, as dictated by the properties of the metallic thin films.
References Section 3.2.A:
[1] T. Kampfrath, et al. Terahertz spin current pulses controlled by magnetic heterostructures, Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 256-260 (2013).
[2] E. T. Papaioannou, et al. Efficient terahertz generation using Fe/Pt spintronic emitters pumped at different wavelengths, IEEE Trans. Magn. 54, 1-5 (2018).
4. Publications
4.1 Journals
- S. Macpherson, T. A. S. Doherty, A. J. Winchester, S. Kosar, D. N. Johnstone, Y. Chiang, K. Galkowski, M. Anaya, K. Frohna, A. N. Iqbal, S. Nagane, B. Roose, Z. Andaji-Garmaroudi, K. W. P. Orr, J. E. Parker, P. A. Midgley, K. M. Dani and S. D. Stranks, Local nanoscale phase impurities are degradation sites in halide perovskites, Nature 607, 294-300 (2022).
- V. K. Mag-usara, M. C. Escaño, C. E. Petoukhoff, G. Torosyan, L. Scheuer, J. Madéo, J. Afalla, M. L. Talara, J. E. Muldera, H. Kitahara, D. R. Bacon, M. Nakajima, K. M. Dani, E. T. Papaioannou, R. Beigang, and M. Tani, Optimum excitation wavelength and photon energy threshold for spintronic terahertz emission from Fe/Pt bilayer, iScience 25, 7, 104615 (2022).
- J. Madéo, and K. M. Dani, Harmonic generation in confinement, Nat. Phys. (2022).
- A. Liboon Jr, S. R. Cabo, R. B. Unabia, F. R. G. Bagsican, R. T. Candidato Jr, Phase composition, microstructure, and optical characteristics of spin-coated La-TiO2 and Fe-TiO2, physica status solidi (a) (2023).
4.2 Books and other one-time publications
Nothing to report.
4.3 Oral and Poster Presentations
- Dani, K. M. Femto Lasers: Impacting Science, Technology, Art and Health, Japan Chamber of Commerce and Industry of New York, Webinar, New York, USA, Apr (2022)
- Dani, K. M. Imaging photoexcited phenomena in real and momentum space, MSE Colloquium, Seminar, Stanford University, Palo Alta, CA, USA, Apr (2022)
- Dani, K. M. Excitons in two-dimensional semiconductors – a momentum-resolved perspective, MRS Spring Meeting 2022, Invited Talk, Honolulu, HI, USA, May 09-24 (2022)
- Dani, K. M. Multi-dimensional photoemission spectroscopy of semiconductor heterostructures – resolving photoelectrons in space, time, momentum and energy, MRS Spring Meeting 2022, Invited Talk, Honolulu, HI, USA, May 09-24 (2022)
- Kosar, S., Winchester, A. J., Doherty, T. A. S., Macpherson, S., Petoukhoff, C. E., Frohna, K., Anaya, M., Chan, N. S., Madéo, J., Man, M. K. L., Stranks, S. D., Dani, K. M., The varied nature and roles of nanoscale defects in solution processed triple cation mixed halide perovskite thin films, International Conference on Hybrid and Organic Photovoltaics 2022, Oral Presentation, Valencia, Spain, May 19-25 (2022)
- Bagsican, F. R., Out-of-equilibrium dynamics in electrically-biased CNT networks, International Workshop on Terahertz Nanoscience, Invited Talk, Osaka University, Osaka, Japan, Jun 9th (2022)
- Dani, K. M. Probing the momentum resolved dynamics of excitons in 2D semiconductors, CLEO PR, Invited Talk, Sapporo, Japan, Jul 31- Aug 05 (2022)
- Dani, K. M. Exploring Excitonic Excitations in Momentum Space, The 4th International Workshop on Quantum Matter- Quantum Many-body Dynamics, Invited Talk, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, Aug 22-26 (2022)
- Dani, K. M., Imaging Photoinduced Phenomena – in real and momentum space, Seminar, Physics Dept., École Normale Supérieure Paris, France, Sep (2022)
- Dani, K. M., Imaging Photoinduced Phenomena – in real and momentum space, Colloquium, Phys. & Chem. Dept. Philipps Universität, Marburg, Germany, Sep (2022)
- Dani, K. M., Exploring Excitonic Excitations in Momentum Space, The Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft e. V. (2022 DPG Meeting), Invited Talk, University of Regensburg, Regensburg, Germany, Sep 06-08 (2022)
- Man, M. K. L., Madéo, J., Karni, O., Barré, E., Georgaras, J., Sahoo, C., Campbell, M., Pareek, V., Wong, E. L., Bacon D., Zhu, X., Ribeiro, H. B., O’Beirne, A. L., Hu, J., Al Mahboob, A., Chan, N. S., Karmakar, A., Winchester, A. J., Kim, B., Watanabe, K., Taniguchi, T., Barmak, K., Jornada, F. H., Li, X., Heinz, T. F., Cao, T., Dani, K. M., Capturing the wavefunction of excitons in 2D semiconductors, The 92nd IUVSTA workshop on Advanced Spectroscopy and Transport for 2D Materials at Surfaces and The 4th Asia-Pacific Symposium on Solid Surfaces (APSSS-4), Invited talk, OIST, Okinawa, Japan, Sep 18-21 (2022)
- Man, M. K. L., Kosar, S., Winchester, A. J., Doherty, T. A. S., Macpherson, S., Petoukhoff, C. E., Frohna, L., Anaya, M., Chan, N. S., Madéo, J., Stranks, S. D., Dani, K. M., The varied nature and roles of nanoscale surface defects in perovskite thin films, Poster Presentation, The 12th International Conference on LEEM PEEM (LEEM/PEEM 12), Córdoba, Spain, Sep 26-30 (2022)
- Man, M. K. L., Madéo, J., Karni, O., Barré, E., Georgaras, J., Sahoo, C., Campbell, M., Pareek, V., Wong, E. L., Bacon D., Zhu, X., Ribeiro, H. B., O’Beirne, A. L., Hu, J., Al Mahboob, A., Chan, N. S., Karmakar, A., Winchester, A. J., Kim, B., Watanabe, K., Taniguchi, T., Barmak, K., Jornada, F. H., Li, X., Heinz, T. F., Cao, T., Dani, K. M., Momentum degree of freedom of excitons in 2D semiconductors, Oral Presentation, The 12th International Conference on LEEM PEEM (LEEM/PEEM 12), Córdoba, Spain, Sep 26-30 (2022)
- Dani, K. M., Imaging Photoinduced Phenomena – in real and momentum space, Stanford Linear Acc. (SLAC) User Meeting, Invited Talk (online), Palo Alto, CA, USA Sep (2022)
- Dani, K.M., Multi-dimensional photoemission electron spectroscopy – resolving the photoemitted electron in space, time, energy and momentum, Instrumentation Colloquium, LBNL, Berkeley, CA, USA, Oct (2022)
- Dani, K.M., Exploring Excitonic Excitations in Momentum Space, International Workshop on Nitride Semiconductors (IWN), Invited Talk, Berlin, Germany, Oct 09-14 (2022)
- Dani, K.M., Through the lens of a Momentum Microscope – Imaging excitons in 2D semiconductors, 14th International Symposium on Atomic Level Characterization (ALC ’22), Invited Talk, Okinawa, Japan, Oct 16-21 (2022)
- Bagsican, F.R., Out-of-equilibrium dynamics in electrically-biased carbon nanotubes, 40th SPP Physics Conference and Annual Meeting, Invited Talk, Legazpi City, Albay, Philippines, Oct 19-21 (2022)
- Dani, K.M., Probing the impact of nanoscale defect sites in perovskite photovoltaics with time-resolved photoemission electron microscopy, The 58th Annual American Vacuum Society (AVS) International Symposium & Exhibition, Invited Talk, PA, USA, Nov 06-11 (2022)
- Bagsican, F.R., Probing out-of-equilibrium dynamics in carbon nanotubes using terahertz emission, International Conference on Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Invited Talk, Butuan City, Philippines, Dec 08-09 (2022)
- Dani, K.M., Imaging photo-induced phenomena – in real and momentum space, PersephoNe Winter School, Invited Talk, Bormio, Italy, Jan 08-13 (2023)
- Lisicovas, V., Mini Femtosecond Laser Driven Surgical Catheter, TR Promotion Joint Forum Life Science Technology Exchange Meeting, Poster Presentation, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, Feb 28th (2023)
- Pareek, V., Bacon, D., Zhu, X., Chan, Y.H., Bussolotti, F., Chan, N.S., Urquizo, J.P., Watanabe K., Taniguchi, T., Man, M.K.L., Madéo, J., Qiu, D., Eng K., Goh, J., Jornada, F.H., Dani, K.M., Time-Resolved ARPES Study of Floquet-Bloch States in Monolayer Tungsten Disulfide, APS March Meeting 2023, Oral Presentation, Las Vegas, Nevada, U.S.A., Mar 05-10 (2023)
- Zhu, X., Bacon, D., Pareek, V., Urquizo, J.P., Chan, N.S., Bussolotti, F., Watanabe, K., Taniguchi, T., Man, M.K.L., Madéo, J., Goh, J., Dani, K.M., Study of momentum-resolved exciton and free carrier properties in monolayer WS2, Oral Presentation, APS March Meeting 2023, Las Vegas, Nevada, U.S.A., Mar 05-10 (2023)
5. Intellectual Property Rights and Other Specific Achievements
Nothing to report.
6. Meetings and Events
6.1 Seminar
- Ruotian Chen, Imaging photoinduced charge transfer in photocatalyst particles with surface photovoltage techniques, Internal Seminar (online), OIST B503 Feb 1st (2023)
- Jianhui Fu, Time-resolved electron-phonon interactions in 2D halide perovskites, Internal Seminar (online), OIST A618 Feb 27th (2023)
- Joanna Nadolna, Visible-light-driven lanthanide modified TiO2 photocatalyst utilizing up-conversion effect, Internal Seminar (online), OIST A613, Mar 15th (2023)
- Oleg P. Dimitriev, Unusual photophysics of near-infrared tricarbocyanine dyes; From anti-Stokes to anti-Kasha emission, Internal Seminar, OIST B513, Mar 22nd (2023)
- Takumi Fukuda, Ultrafast electron and lattice dynamics in two-dimensional layered transition-metal dichalcogenides, Internal Seminar, OIST C209, Mar 30th (2023)
6.2 Workshop
Nothing to report.
7. Other
7.1 Award
- Bagsican, F. R., 16th Osaka University Kondo Prize (Research Paper Award), Terahertz Excitonics in Carbon Nanotubes: Exciton Autoionization and Multiplication, Jun 22nd (2022)
- Pareek, V., Ovshinsky Student Travel Award, Division of Material Physics (DMP), APS March meeting 2023, Mar 7th (2023)



