FY2020 Annual Report
Integrated Open Systems Unit
Professor Hiroaki KITANO
Abstract
Integrated Open Systems Unit has launched a new project, "Laboratory Automation with AI Robotics." Our challenge aims to build novel forms of a research experimental platform that would accelerate scientific discovery by blending robotics and AI technologies. In FY2020, as the first year of this new initiative, we introduced a couple of different experimental robots and assembled their operation testing environment.
The Open Energy System (OES) project has moved to the next phase, the actual operation. After completing the demonstrative research on the hillside faculty housing area we had been conducting since 2014, all OES facility equipment and the system had transferred under the management of OIST.
1. Staff
- Kenichiro ARAKAKI, Research Unit Technician
- Sachie YUKAWA, PhD Student
- Tomoko YOSHINO, Research Unit Administrator
2. Collaborations
2.1 Distributed DC power control to realize the Open Energy System
- Description: Implementation and Evaluation of a DC microgrid with energy sharing features
- Type of collaboration: Joint research
- Researchers: Researchers from Sony Computer Science Laboratories
3. Activities and Findings
3.1 Robots for the Laboratory Automation
Laboratory automation involves a wide variety of laboratory equipment working tandemly together to run experimental protocols.
In FY2020, we introduced two kinds of single-arm vertical articulated robots (single-arm 6-axis robots) at the OIST measurement equipment room (B522).
One is an industrial robot (Figure 1), which works with many varieties of inspection and analysis equipment in the laboratory to perform Machine-to-Machine (M2M) factory-like automation of self-completable experimental procedures.
The other is a collaborative robot (Figure 2), which primarily performs experiments automation conducted by scientists and machines in collaboration.
These robots and lab equipment will be connected and controlled, foundation by the same platform to automate various experimental protocols.
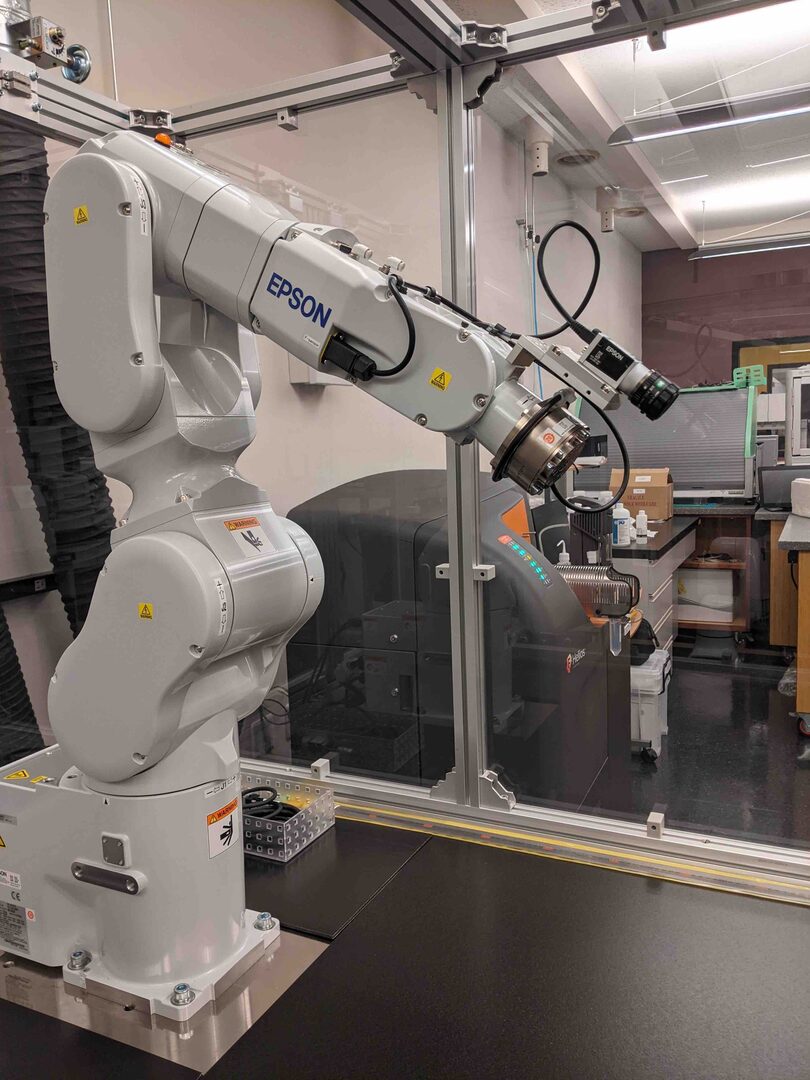

Figure 1: Seiko Epson Corporation (EPSON), C8-A901S Industrial Robot with GigE Camera Vision Guide and Force Guide systems. A Robot Hand End-Effector is scheduled to be implemented next year.
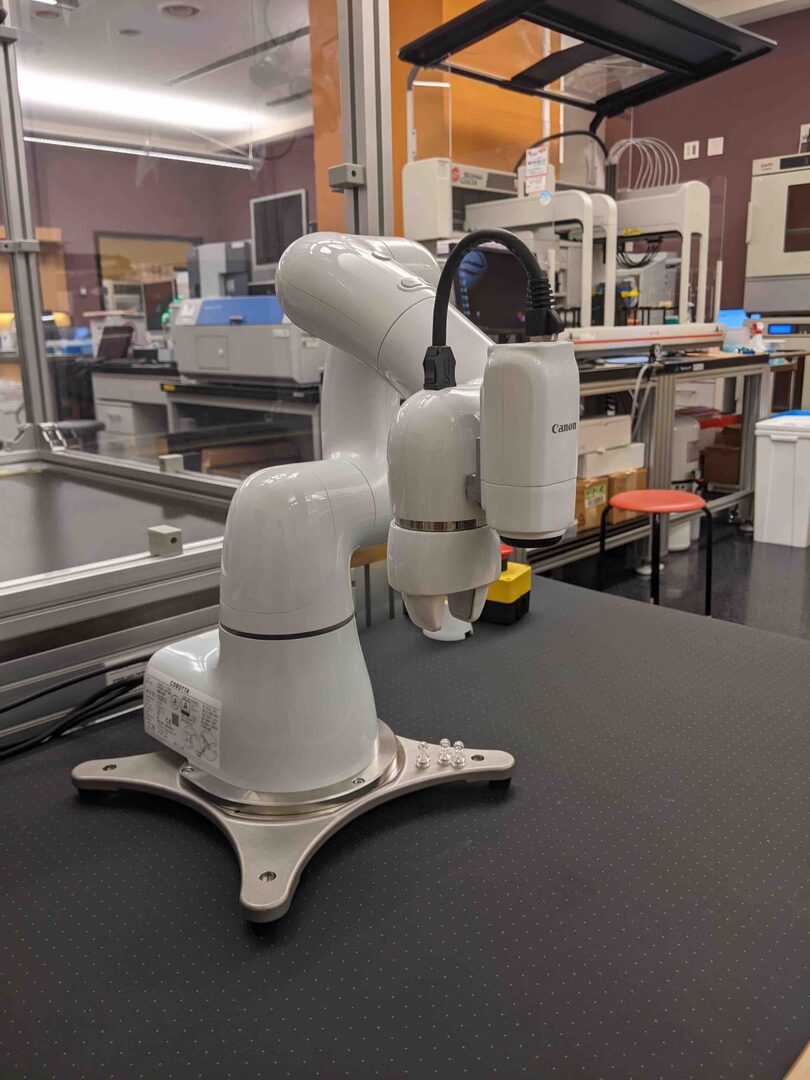

Figure 2: DENSO WAVE Incorporated (DENSO), COBOTTA Collaborative Robot with AF Camera vision.
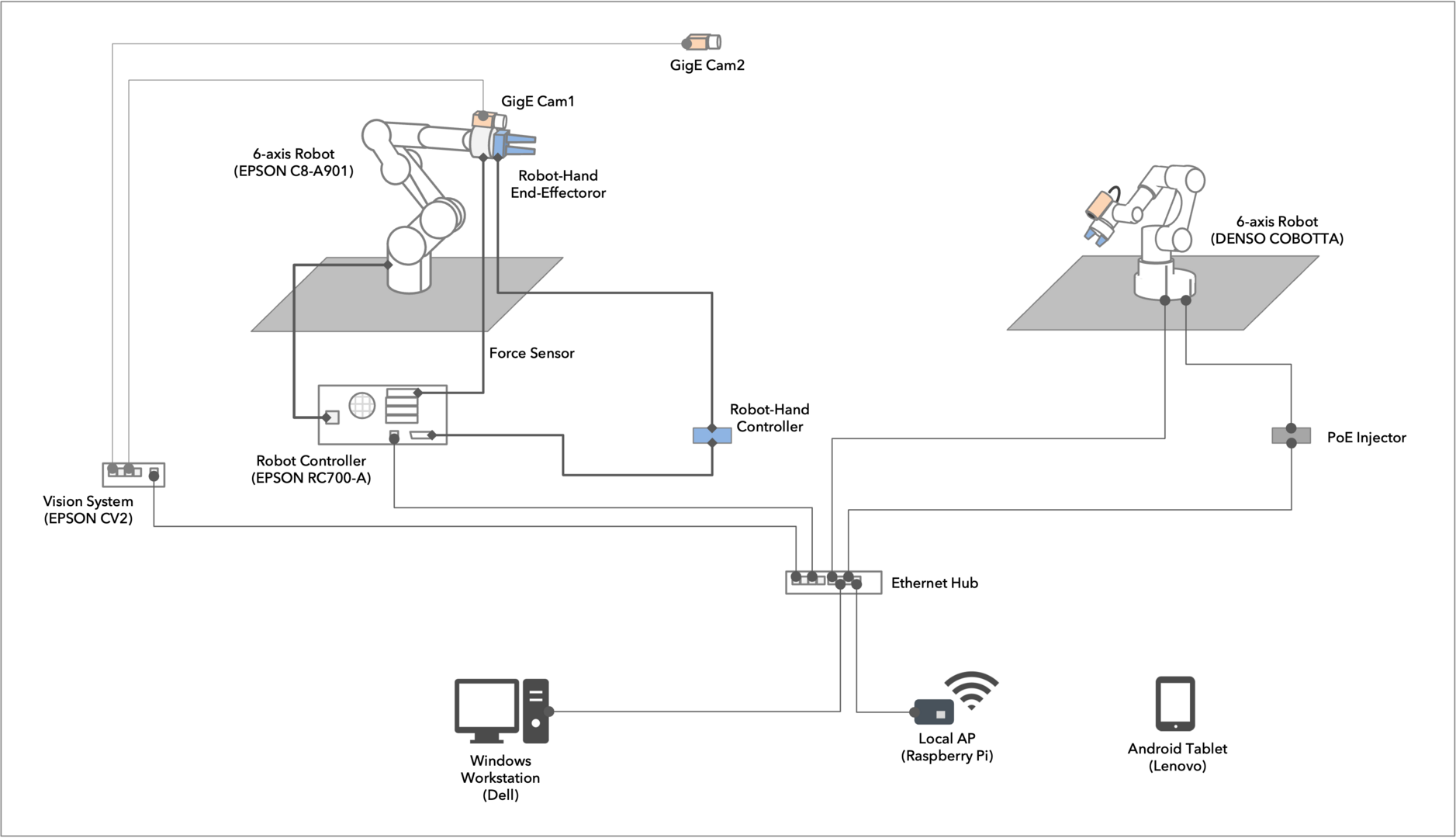
Figure 3: Robot System Connection Diagram (Testing Environment)
3.2 Feasibility survey toward Laboratory Automation
Toward the laboratory automation, we investigated the status of the tests and experiments currently being carried out or planned in the on-campus laboratory and that for aiming to extract the points and issues that might be useful for automation.
COVID-19 PCR TEST
OIST is conducting a PCR test of COVID-19 in cooperation with Okinawa Prefecture Government (OPG) to contribute to measures against the spread of coronavirus infection. DNA Sequencing Section (SQC) in the Research support division and Occupational Health and Safety Section (OHS) play a central role in this operation at OIST. Outcomes from the discussion in a hearing survey from SQC were more operational reforming challenges in the sample acceptance than the testing process. Therefore, we considered the PCR test automation model (Figure 5) and shared it with SQC members.
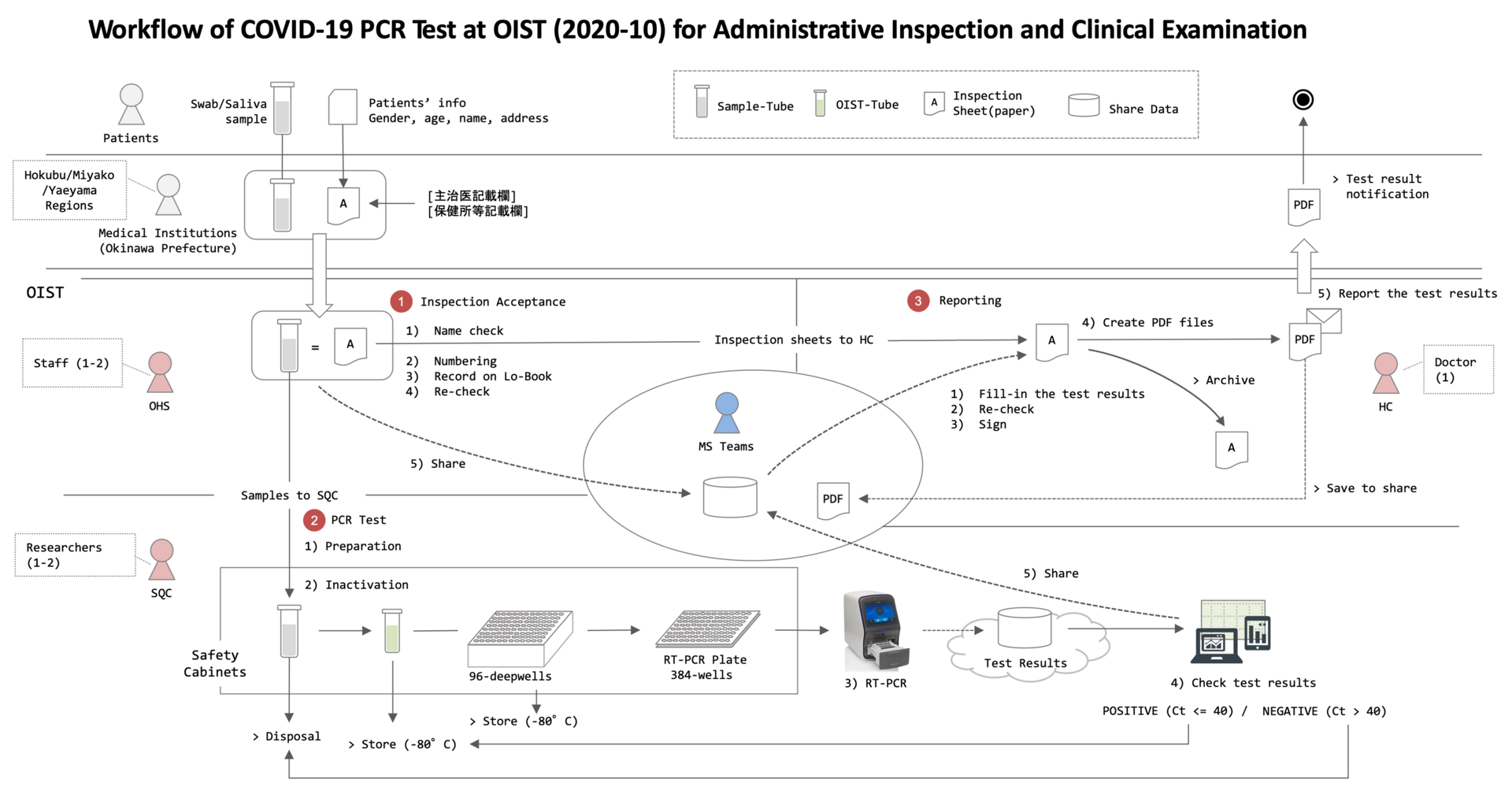
Outline of COVID-19 PCR Test Workflow
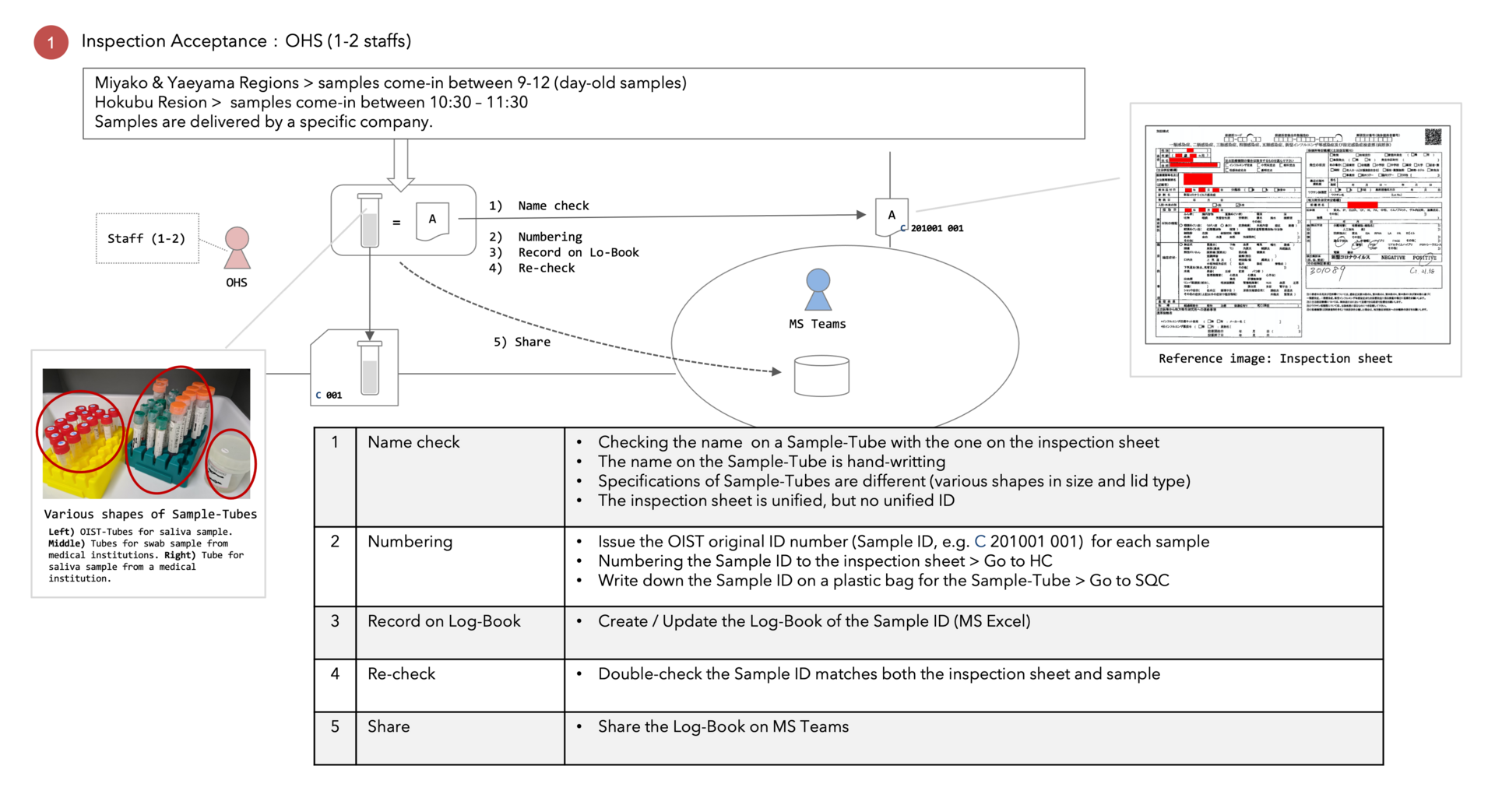
1) Inspection acceptance
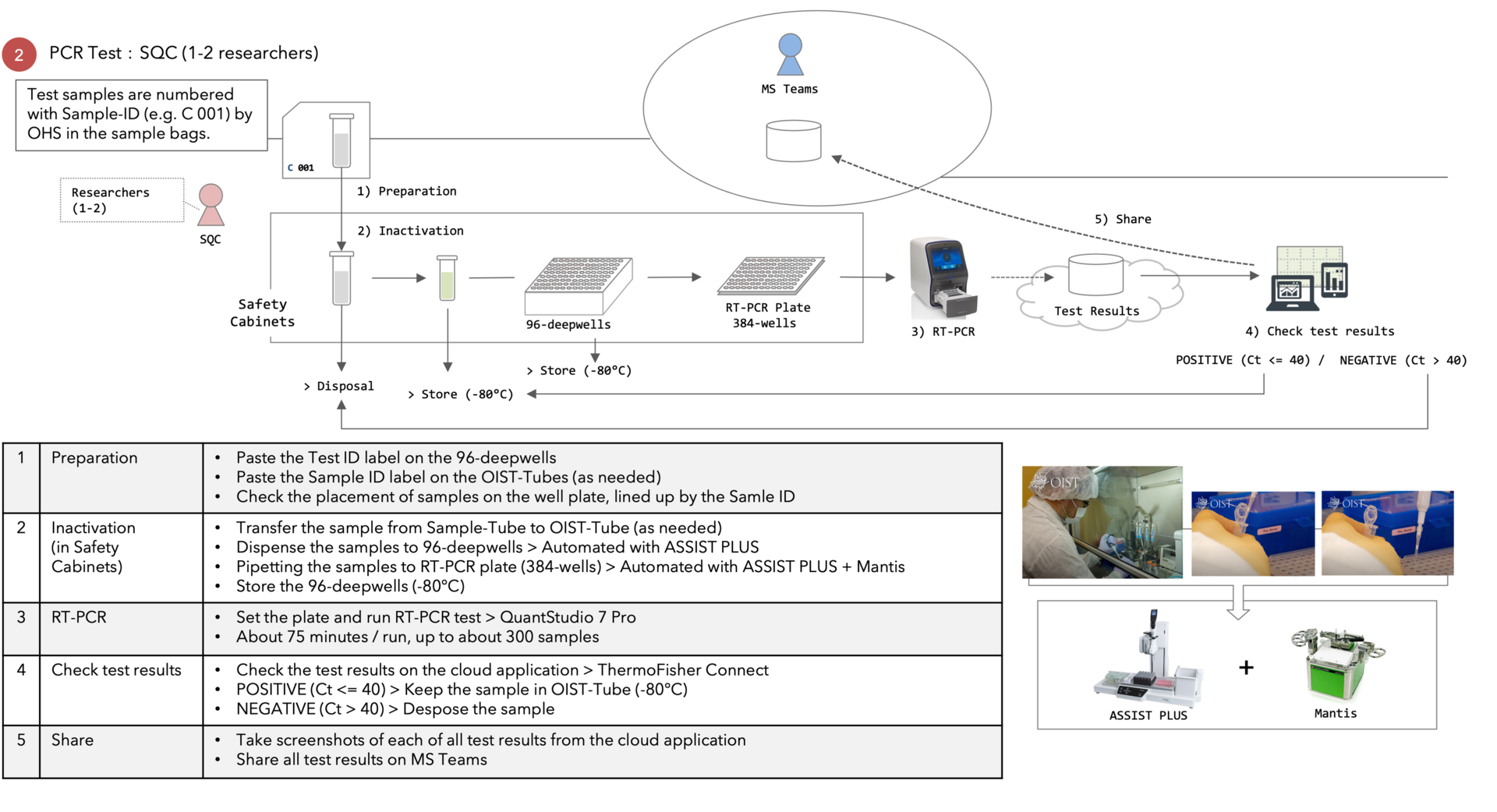
2) PCR Test
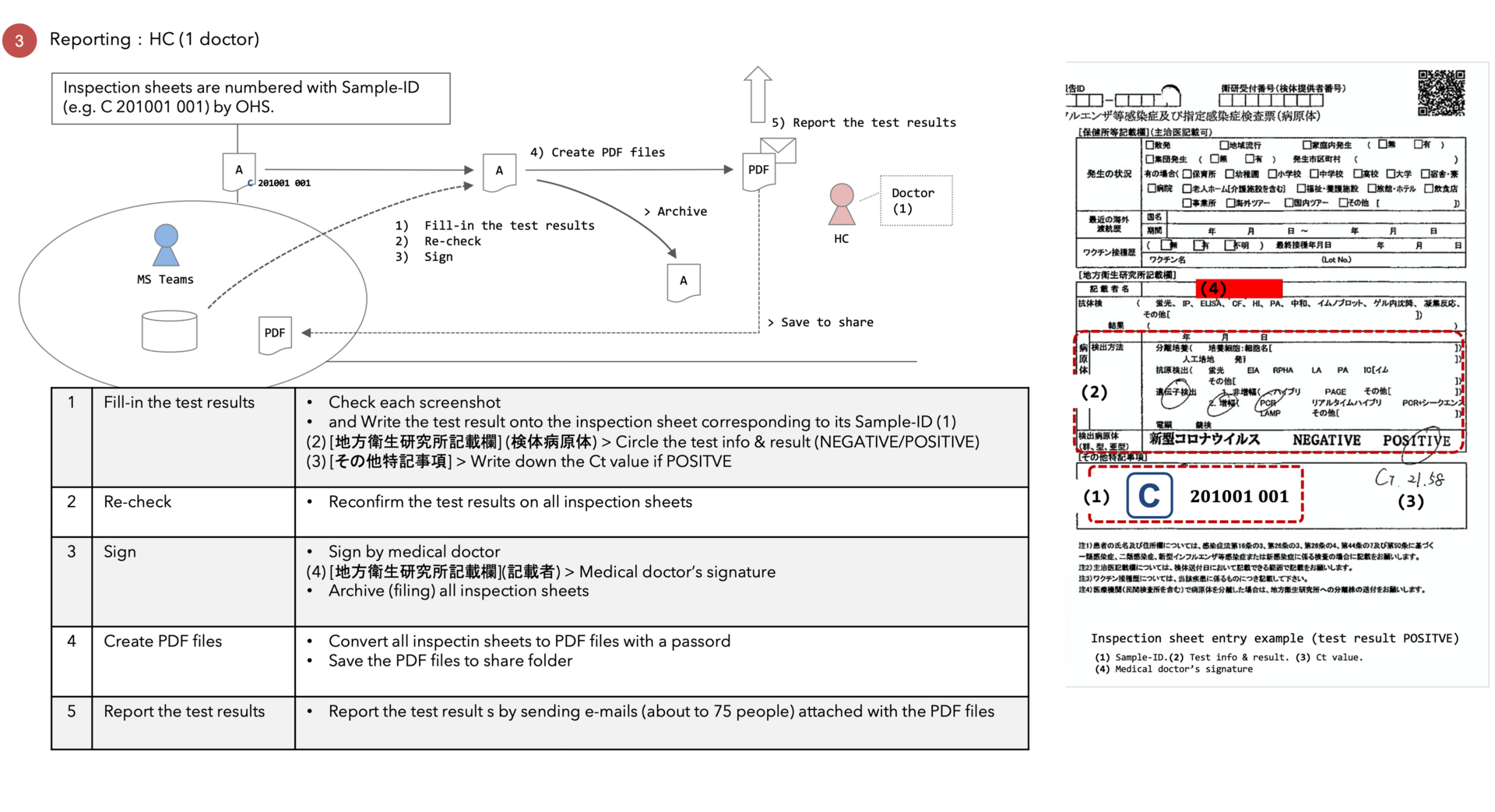
3) Reporting
Figure 4: COVID-19 PCR Test Workflow at OIST (2020-10)
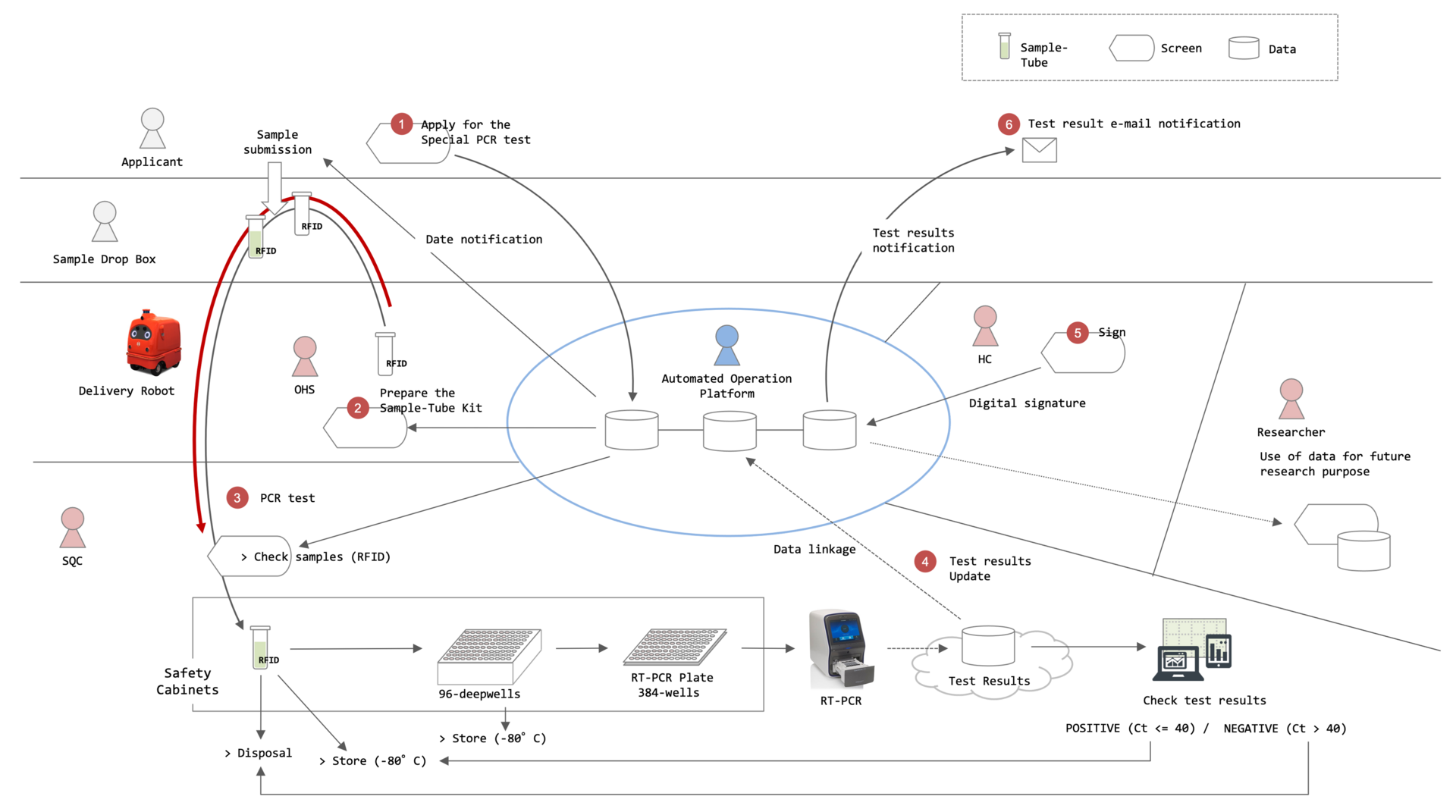
Figure 5: Outline Image of COVID-19 PCR Test Automation Model at OIST
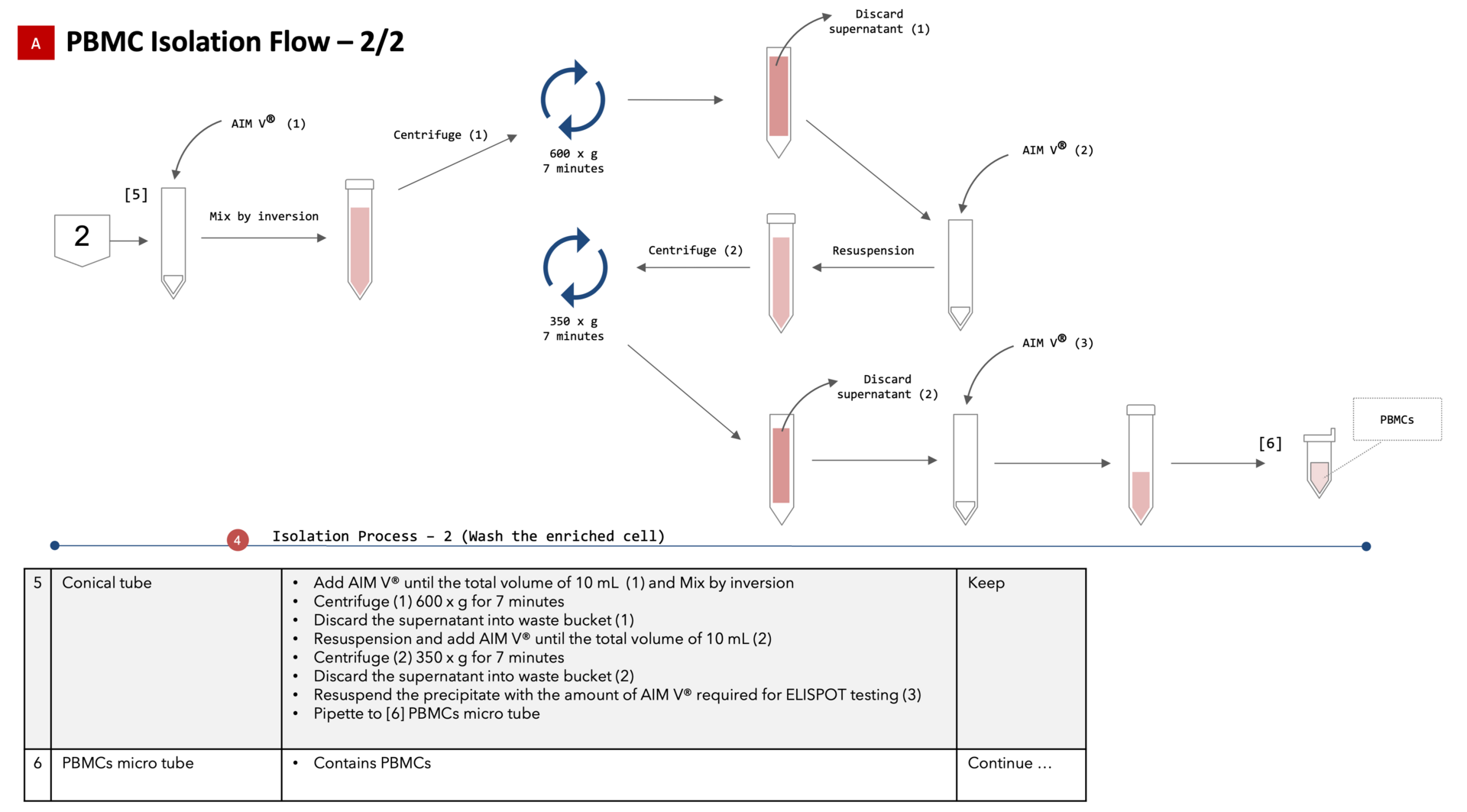
PBMC Isolation
Regarding the COVID-19 T-Cell Project promoted by the Immune Signal Unit (Ishikawa Unit), we collaborated to examine the automation of the experiment assays in the project. In the experiment, peripheral blood mononuclear cells are isolated from whole blood samples, and SARS-Cov-2- specific T-cell quantification analysis and T-cell phenotype analysis are performed by ELISpot and Flow Cytometry assays, respectively.
This year, we examined automation, focusing on the PBMC isolation protocol currently being performed manually.
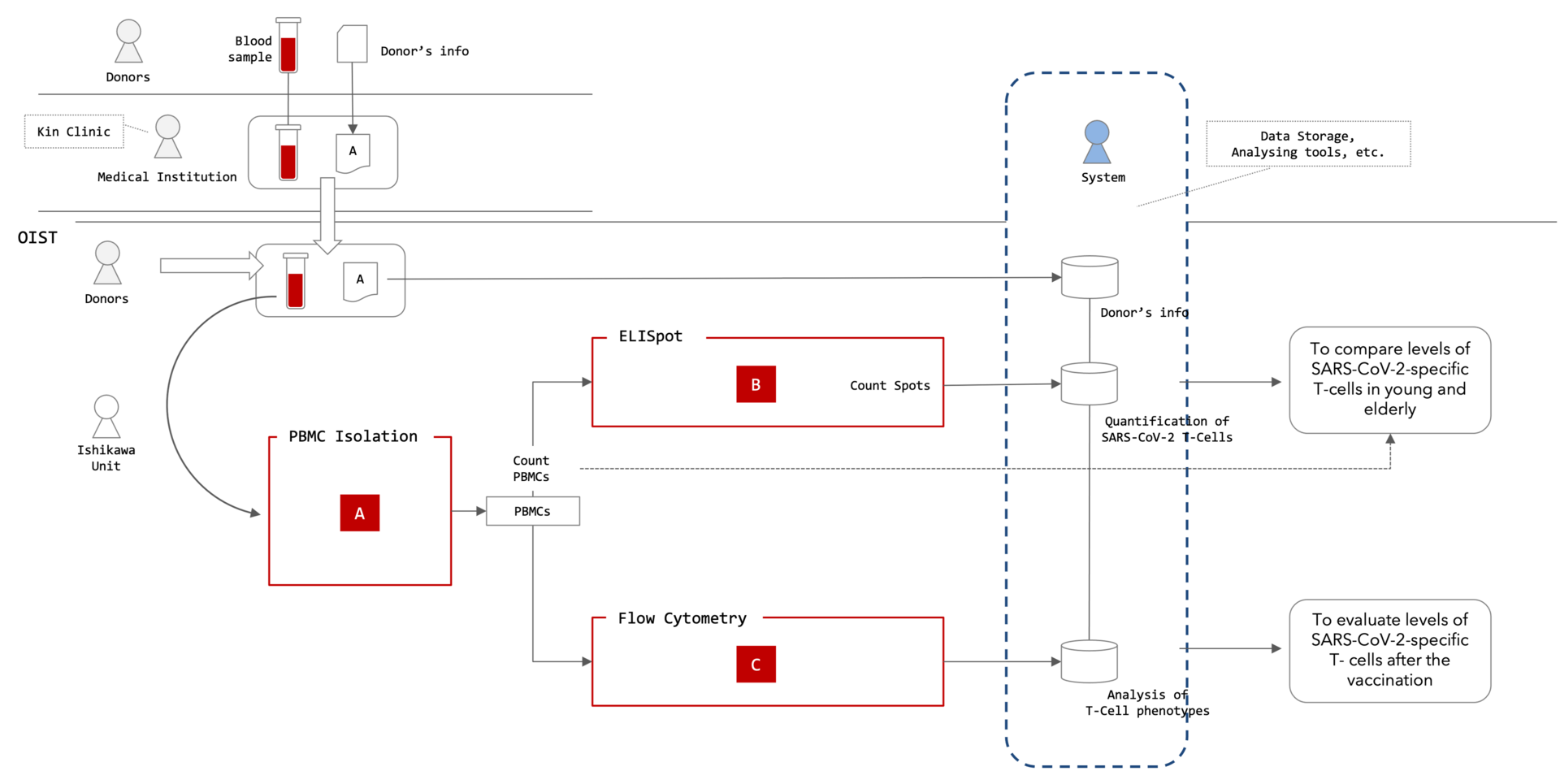
Figure 6: Outline Image of COVID-19 T-Cell Project Experimental Flow
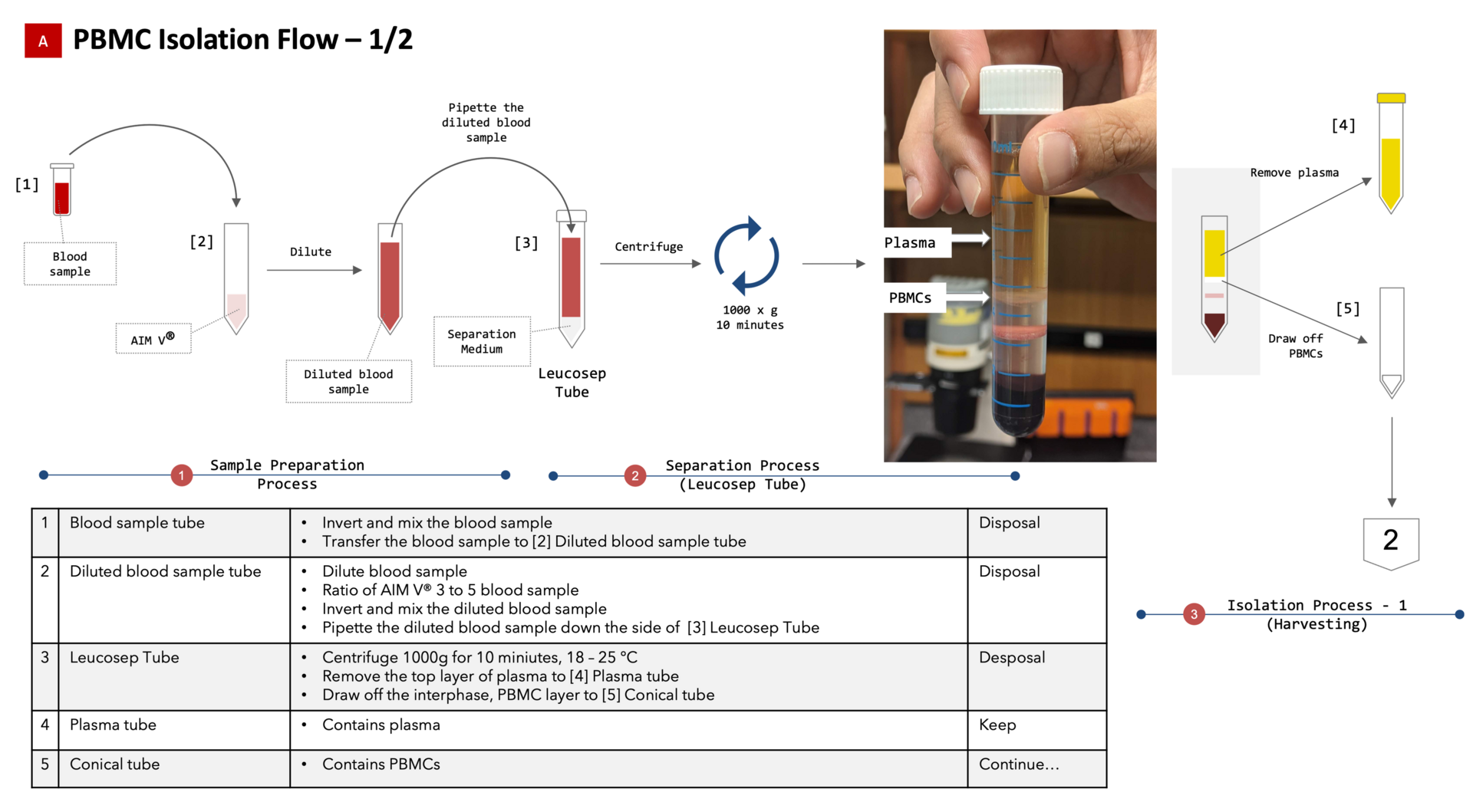
PBMC Isolation flow 1/2
PBMC Isolation Flow 2/2
Figure 7: PBMC Isolation Flow

Figure 8: PBMC Isolation Automation Outline Image
3.3 Open Energy System
The Open Energy System (OES) community in the hillside faculty housing area has been separated into three communities and will be newly operated. Along with this, we rebuilt the logging system and fault detection alert system of all communities.
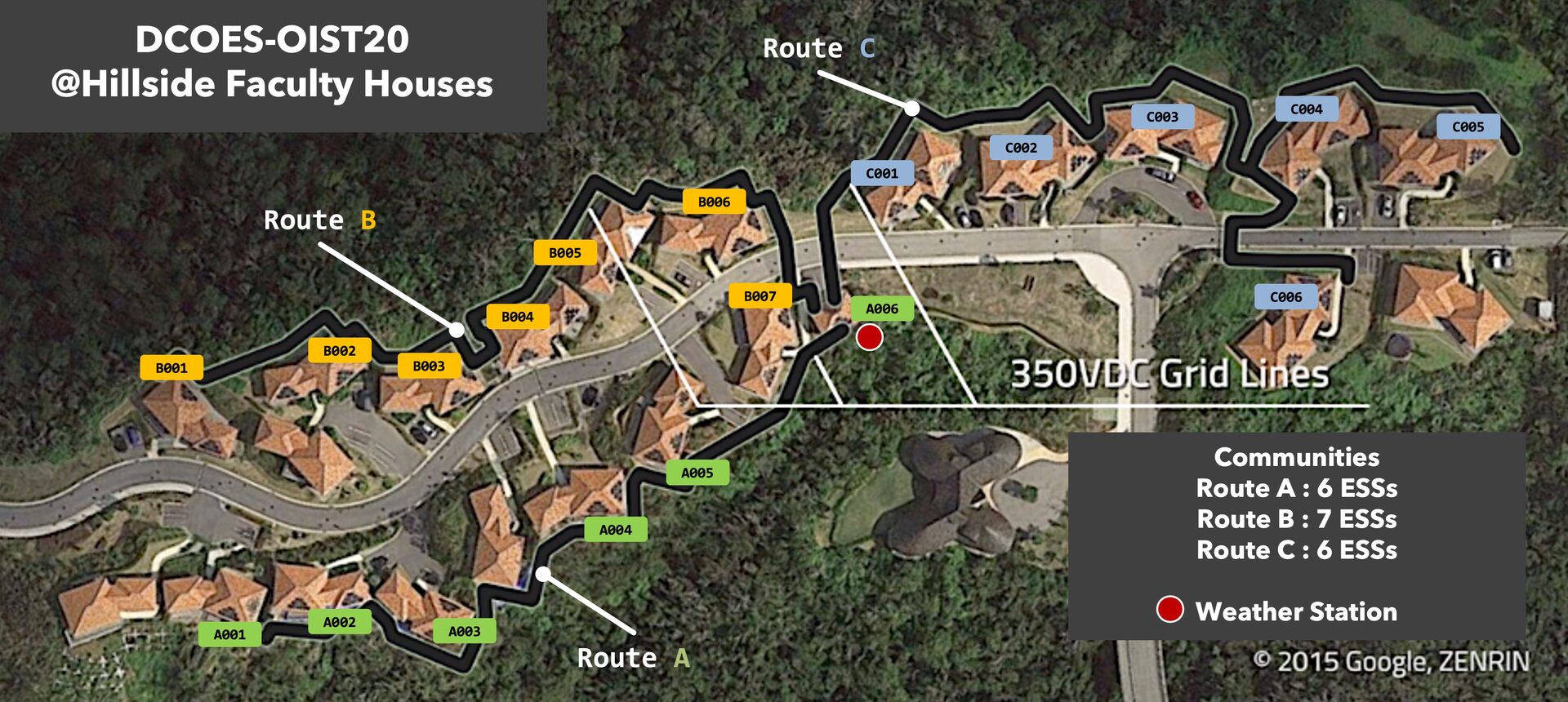
Figure 9: Open Energy System at OIST Hillside Faculty Housing
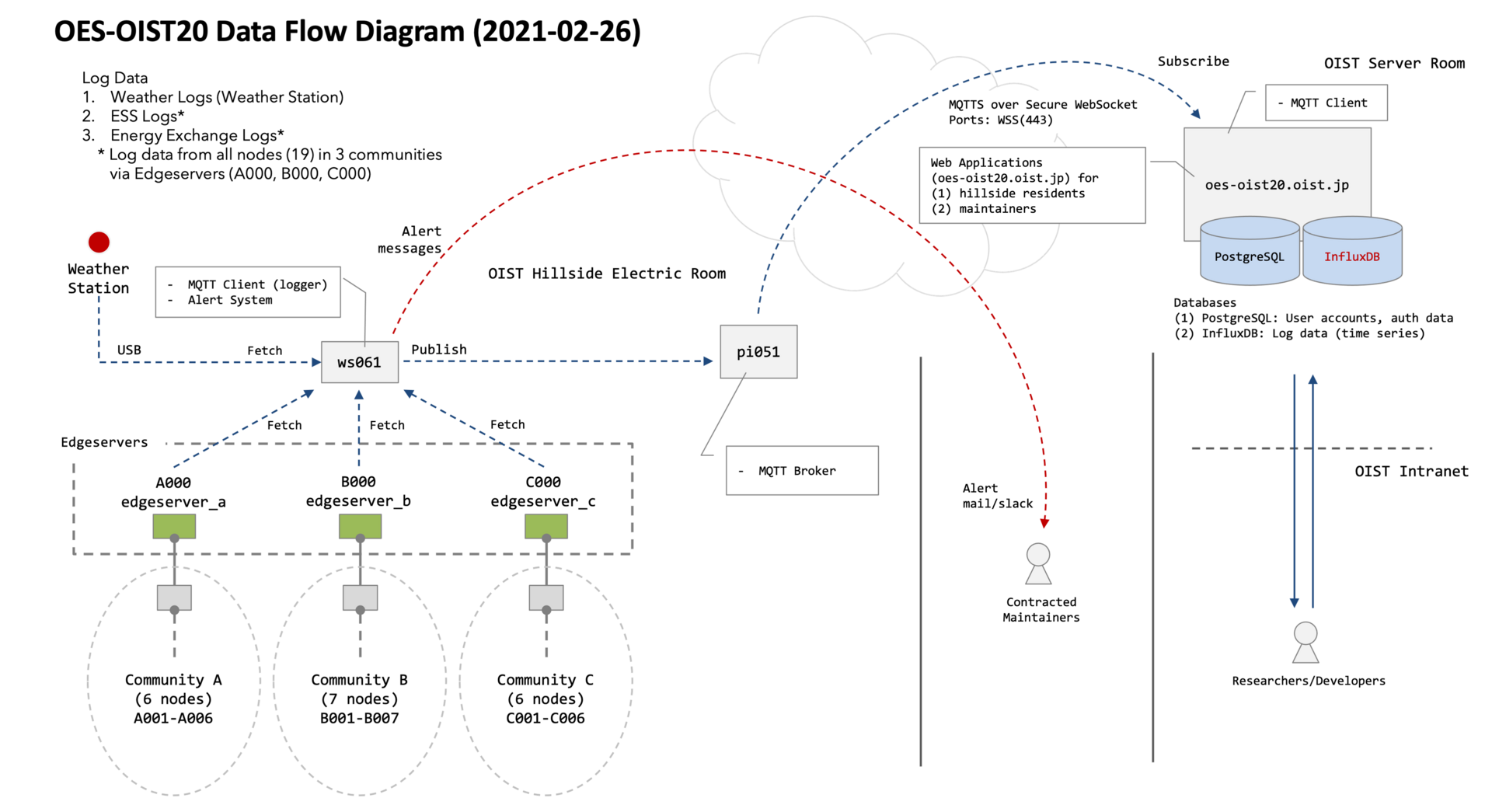
Figure 10: Open Energy System Data Flow Diagram at OIST Hillside Faculty Housing
4. Publications
4.1 Journals
- Marek Ostaszewski, Alexander Mazein, Marc E. Gillespie, Inna Kuperstein, Anna Niarakis, Henning Hermjakob, Alexander R. Pico, Egon L. Willighagen, Chris T. Evelo, Jan Hasenauer, Falk Schreiber, Andreas Dräger, Emek Demir, Olaf Wolkenhauer, Laura I. Furlong, Emmanuel Barillot, Joaquin Dopazo, Aurelio Orta-Resendiz, Francesco Messina, Alfonso Valencia, Akira Funahashi, Hiroaki Kitano, Charles Auffray, Rudi Balling & Reinhard Schneider, COVID-19 Disease Map, building a computational repository of SARS-CoV-2 virus-host interaction mechanisms, Scientific Data, volume 7, Article number: 136 (2020), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-020-0477-8
- Richard Nock, Natalia Polouliakh, Frank Nielsen, Keigo Oka, Carlin R. Connell, Cedric Heimhofer, Kazuhiro Shibanai, Samik Ghosh, Ken-ichi Aisaki, Satoshi Kitajima, Jun Kanno, Taketo Akama, Hiroaki Kitano, A Geometric Clustering Tool (AGCT) to robustly unravel the inner cluster structures of time-series gene expressions, PLOS ONE, 15(7): e0233755, July 6, 2020, Peer-Reviewed
- Akinori Nishi, Katsuya Ohbuchi, Noriko Kaifuchi, Chika Shimobori, Hirotaka Kushida, Masahiro Yamamoto, Yoshihiro Kita, Suzumi M. Tokuoka, Ayako Yachie, Yukiko Matsuoka, Hiroaki Kitano, LimeMap: a comprehensive map of lipid mediator metabolic pathways, npj Systems Biology and Applications, 7, Article number: 6 (2021), 27 January 2021,https://doi.org/10.1038/s41540-020-0016
4.2 Books and other one-time publications
Nothing to report
4.3 Oral and Poster Presentations
[Oral presentations]
- Hiroaki Kitano, Setting ‘Moonshots’ on Target: U.S.-Japan Strategies for National Technology Investment, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace Japan Moonshot symposium, Online Symposium, May 28, 2020.
- Hiroaki Kitano, Creating the Engine for Scientific Discovery: A Case on AI -Driven Systems Pharmacology, the virtual PS-Chugai Modelling & Simulation symposium, Chugai, virtual Symposium, June 15, 2020.
- Hiroaki Kitano, Toward the Automation of Scientific Discovery by AI and Robotics, ISSCR 2020, the International Society for Stem Cell Research, virtual, June 25, 2020
- Hiroaki Kitano / 北野宏明, Impact of Paradigm Change after COVID-19 on the Future of Health Society /コロナ禍によるパラダイムチェンジで未来の健康社会に向けて何が変わる, LINK-J(オンライン国際シンポジウム) / LINK-J(Online International Symposium), May. 12, 2020.
- Hiroaki Kitano/北野宏明, Pandemic and AI: Building Pandemic-Ready Society, NVIDIA COVID-19 Webinar / AI/HPC が切り拓く COVID-19 研究最前線 ~予防・治療から社会変容への対応まで~, Tokyo Webinar, 東京 ウェビナー, Aug 6,2020
- Hiroaki Kitano, Creating the Engine for Scientific Discovery: Nobel Turing Challenge as a Grand Challenge project in AI and Systems Biology, TW-E4R Symposium 2020, Webinar, India, Oct 11, 2020
- Hiroaki Kitano, Nobel Turing Challenge : A Grand Challenge on AI for Scientific Discovery, International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence and Brain Science 2020, Online, Tokyo, Oct 12, 2020
- Hiroaki Kitano, Creating the Engine for Scientific Discovery: Nobel Turing Challenge as a grand challenge project in AI and broader science and technology fields, 3rd joint seminar of JST and STM: The Transformation in scholarly publishing: Research Data, virtual, Tokyo, Oct 27, 2020
- Hiroaki Kitano, Japan's Moon shot goals and its background, Sweden Innovation Days, Webinar, Sweden, Nov 17,2020
- Hiroaki Kitano, Nobel Turing Challenge — Creating the Engine of Scientific Discovery, ICM SEMINARS IN COMPUTER AND COMPUTATIONAL SCIENCE, virtual, Poland, Nov 26, 2020
- Hiroaki Kitano, Nobel Turing Challenge: Creating the Engine for Scientific Discovery, SCAI Symposium "Doing Science in the Age of Artificial Intelligence", virtual, Dec 14, 2020
- Hiroaki Kitano, AI in the great reset, The 1st Symposium on Industrial Applications of Artificial Intelligence, online, Tokyo, Dec 15, 2020
- Hiroaki Kitano / 北野宏明, Introduction of moonshot type R & D business in the field of health and medical care / 健康・医療分野におけるムーンショット型研究開発事業の紹介, 3rd Well Aging Society Summit Asia-Japan, Webinar, Tokyo / 東京, Oct 12, 2020
- Hiroaki Kitano / 北野宏明, The turning point of civilization: A Paradigm Shift after COVID-19 pandemic / 文明の転換点: パンデミックが覚醒させたパラダイム転換, the 11th RBS Seminar Ritsumeikan Uni., 立命館大学第11回RBSセミナー「未来をどう見るか、どう創るか」, Webinar, Osaka / 大阪, Nov 14, 2020
- Hiroaki Kitano / 北野宏明, Introducing Garuda Platform / Garuda Platformについて, AMED Seminar / AMED Garuda講演会, virtual, Tokyo Dec 4, 2020
- Hiroaki Kitano / 北野宏明, Creating the Engine for Scientific Discovery, 16th JAMTTC Translational Research Workshop / 第16回トランスレーショナルリサーチワークショップ, Webinar, Tokyo, Jan 19, 2021(invited)
- Hiroaki Kitano / 北野宏明, The turning point of civilization / 文明の転換点, Special lecture for POLA, POLA特別講演, online, Tokyo, Feb 4, 2021(invited)
- Hiroaki Kitano / 北野宏明, TBD, OIST Forum 2021, online, Tokyo, Mar 3, 2021(invited)
5. Intellectual Property Rights and Other Specific Achievements
Nothing to report
6. Meetings and Events
6.1 Nobel Turing Challenge: Creating the Engine for Scientific Discovery,
- Date: April 20, 2020
- Venue: The Institute of Medical Science The Tokyo University, Online Seminar
Kitano, H. Artificial Intelligence to Win the Nobel Prize and Beyond: Creating the Engine for Scientific Discovery. AI Magazine, 37(1), 39-49, 2016
Kitano, H. Systems Biology: A Brief Overview. Science. 295(5560), 1662-1664, 2002
Kitano, H. Computational Systems Biology. Nature. 420(6912), 206-210, 2002
7. Other
Prof. Kitano has been named a fellow of the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence on February 1, 2021.
Please read the article here



