Code - Fujin - Validation - Immersed Boundary Method - Flexible fiber
A hanging filament under gravity
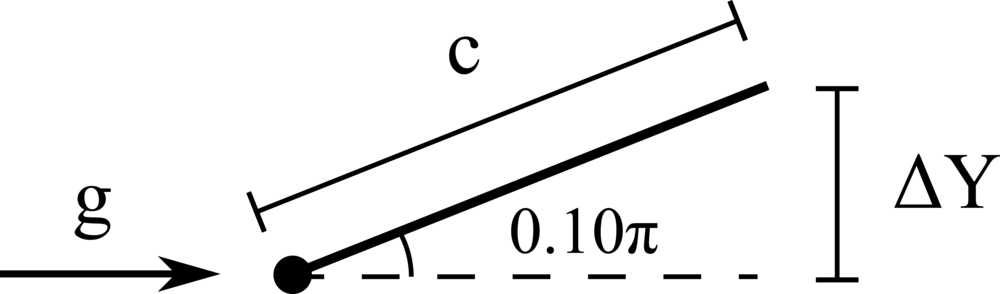
We consider the oscillations of a hanging filament under gravity. A filament of length \(c=1m\), linear density difference \(\Delta \widetilde{\rho}=1 kg/m\) and flexibility \(\gamma=0.01 kg~m^3 / s^2\) is initially held stationary with an angle of \(0.1 \pi\) from the vertical and then, after being released, starts swinging due to the gravity force \(g=10m/s^2\). The filament is discretised with \(100\) Lagrangian points.
config.h
#define _FLOW_CHANNEL_ #define _FLOW_FIXED_ #define _MULTIPHASE_ #define _MULTIPHASE_FIL_ #define _MULTIPHASE_FIL_HING_ #define _MULTIPHASE_FIL_FIXD_
param.f90
! Gravitational acceleration real, dimension(3), parameter :: gr=(/0.0,10.0,0.0/) ! Number of filaments integer, parameter :: filN=1 ! Number of Lagrangian points per filament integer, parameter :: filNL=100 ! Length of the filaments real, parameter :: filL = 1.0 ! Filament linear density difference and flexibility real, parameter :: filDRhoL = 1.0, filGamma=0.01
input/input.in
# Simulation initial and final step 0 200000 # Simulation time 0.0 # Simulation time-step 1.0000000000000001E-004 # Output frequency 1 100000 100 1000000 1000000 # Simulation restart condition for the multiphase part F
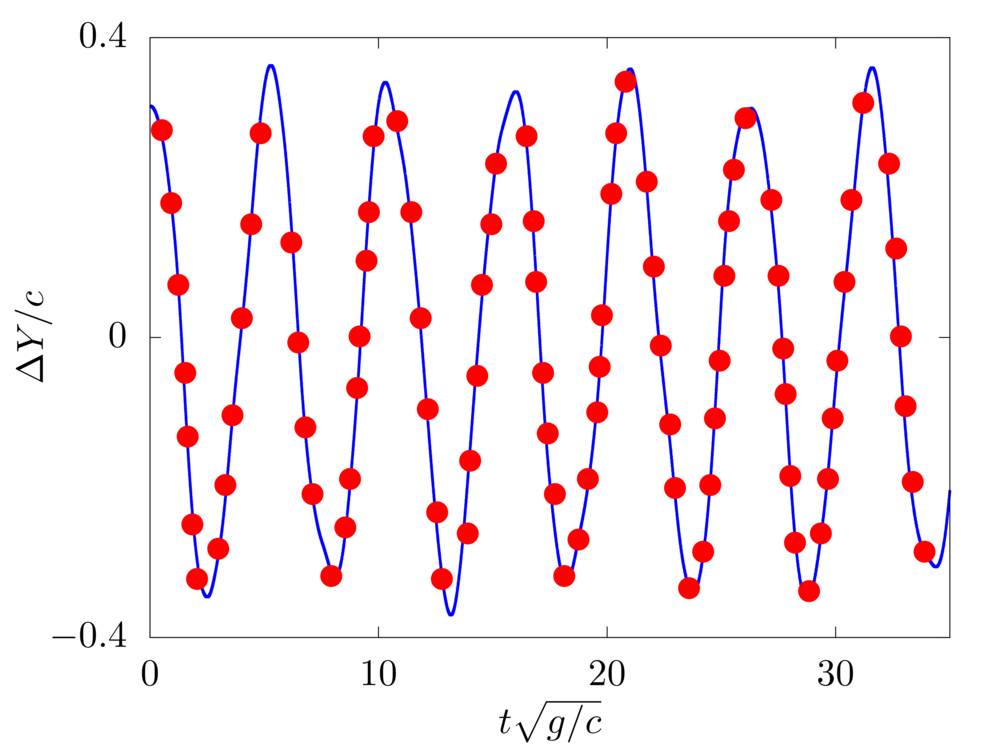
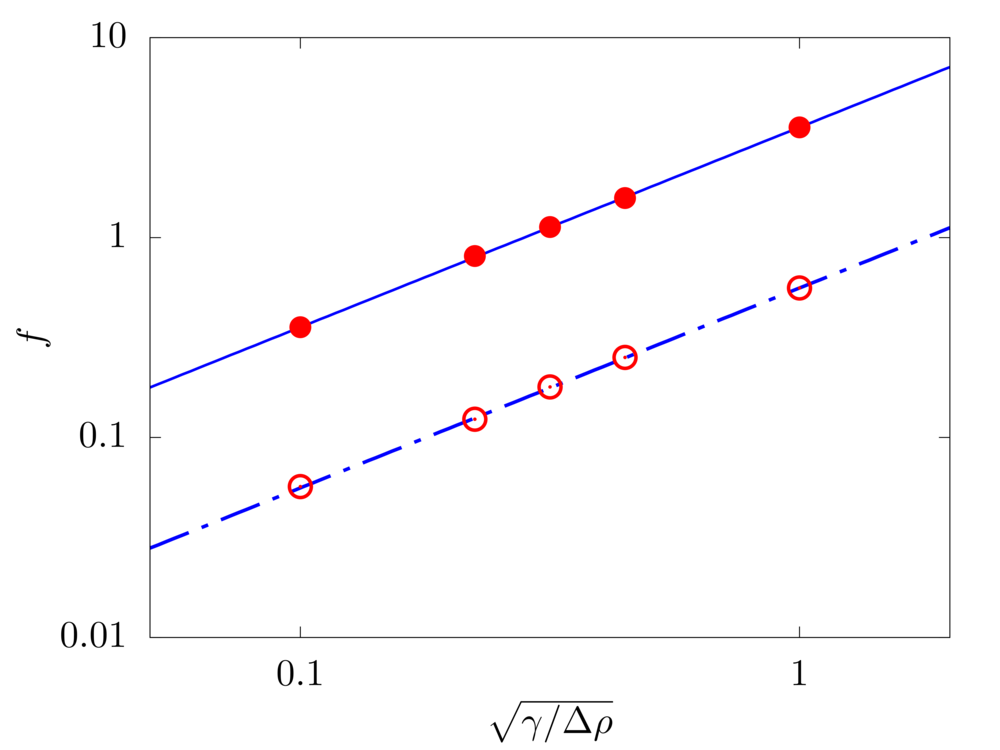
Free vibration of unsupported and cantilevered fibers
In the absence of any load, we evaulate the free vibration of a fiber. The filament length \(c\), flexibility \(\gamma\) and linear density difference \(\Delta \widetilde{\rho}\) are varied and the resulting frequency \(f\) of the free oscillations measured. The filament is discretised with \(100\) Lagrangian points.
Analytical solution - free: \(f = \frac{22.3733}{2 \pi c^2} \sqrt{\frac{\gamma}{\Delta \widetilde{\rho}}}\)
Analytical solution - clamped: \(f = \frac{3.5161}{2 \pi c^2} \sqrt{\frac{\gamma}{\Delta \widetilde{\rho}}}\)
config.h
#define _FLOW_CHANNEL_ #define _FLOW_FIXED_ #define _MULTIPHASE_ #define _MULTIPHASE_FIL_ #define _MULTIPHASE_FIL_FREE_ #define _MULTIPHASE_FIL_FIXD_
param.f90
! Gravitational acceleration real, dimension(3), parameter :: gr=(/0.0,0.0,0.0/) ! Number of filaments integer, parameter :: filN=1 ! Number of Lagrangian points per filament integer, parameter :: filNL=100 ! Length of the filaments real, parameter :: filL = 1.0 ! Filament linear density difference and flexibility real, parameter :: filDRhoL = 1.0, filGamma=0.01
input/input.in
# Simulation initial and final step 0 200000 # Simulation time 0.0 # Simulation time-step 1.0000000000000001E-004 # Output frequency 1 100000 100 1000000 1000000 # Simulation restart condition for the multiphase part F
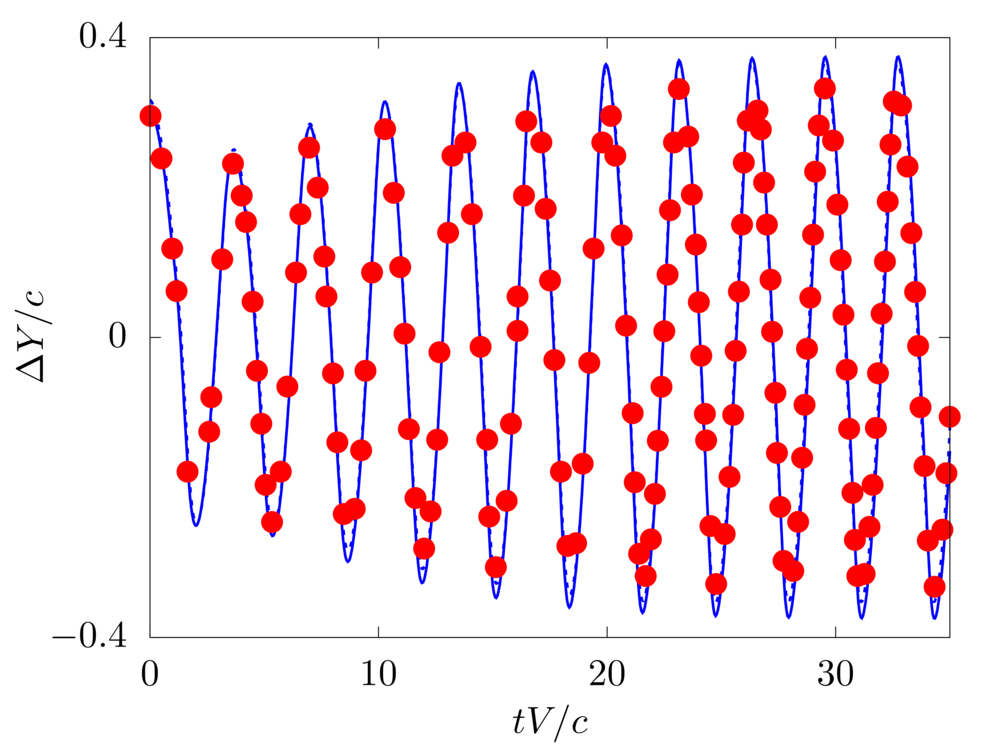
A hanging filament in a uniform flow
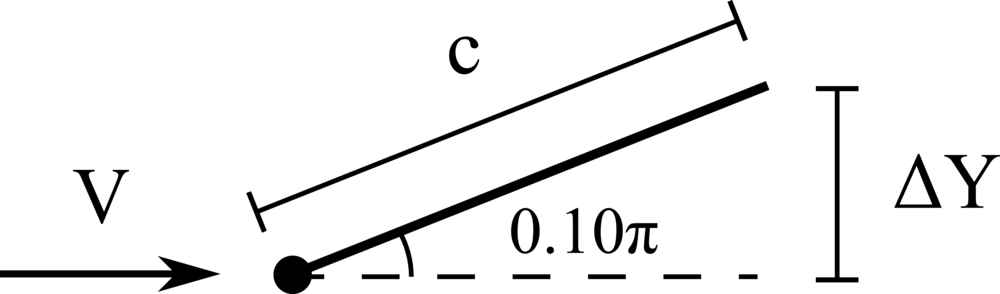
We consider the oscillations of a hanging filament in a uniform flow with velocity \(V\). A filament of length \(c=1m\), linear density difference \(\Delta \widetilde{\rho}=1.5 kg/m\) and flexibility \(\gamma=0.0015 kg~m^3 / s^2\) is initially held stationary with an angle of \(0.1 \pi\) from the vertical and then, after being released, starts swinging due to the combined effect of the viscous fluid flow (\(\nu=0.005m^2/s\)) and gravity force (\(g=0.5m/s^2\)). The filament is discretised with \(65\) Lagrangian points.
config.h
#define _FLOW_INOUT_ #define _FLOW_INOUT_UNBOUND_ #define _SOLVER_INOUT_ #define _MULTIPHASE_ #define _MULTIPHASE_IBML_ #define _MULTIPHASE_IBML_GLDS_ #define _MULTIPHASE_IBML_GLDS_2D_ #define _MULTIPHASE_IBML_XXXX_READ_ #define _MULTIPHASE_IBML_XXXX_FIL_ #define _MULTIPHASE_IBML_XXXX_FIL_HING_
param.f90
! Fluid viscosity and density real, parameter :: vis = 1.0/200.0 real, parameter :: rho = 1.0 ! Reference velocity (bulk velocity or wall velocity) real, parameter :: refVel = 1.0 ! Gravitational acceleration real, dimension(3), parameter :: gr=(/0.0,0.5,0.0/) ! Number of objects integer, parameter :: ibmlN=1 ! Number of Lagrangian points per object integer, parameter :: ibmlNL=65 ! Linear dimension of the object real, parameter :: ibmlL = 1.0 ! Moving or not object logical, parameter :: ibmlMoving = .TRUE. ! Filament linear density difference and flexibility real, parameter :: filDRhoL = 1.5, filGamma=1e-3*filDRhoL
input/input.in
# Simulation initial and final step 0 100000 # Simulation time 0.0 # Simulation time-step 5.0E-004 # Output frequency: 0D, 1D, 2D, 3D, restart data 100 10000 100000 1000000 2000000 # Simulation restart condition for the multiphase part F
References:
[1] W. X. Huang, S. J. Shin, and H. J. Sung. Simulation of flexible filaments in a uniform flow by the immersed boundary method. Journal of Computational Physics, 226(2):2206–2228, 2007.



